The post Why the Apollo 11 Astronauts Went through Customs & Immigration after Entering Earth? appeared first on .
]]>The return of the Apollo 11 astronauts
On 24 July 1969, Neil Armstrong and his fellow astronauts, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins, returned to Earth after completing the Apollo 11 mission. The crew brought their space shuttle down in the Pacific Ocean, 1480 km to the south-west of Hawaii, where the U.S. Navy ship, the USS Hornet, picked them up. It took two days—during which the astronauts remained quarantined in a NASA trailer to prevent the spread of any moon germs and diseases they might have inadvertently brought back. The astronauts emerged from the trailer in biological containment suits and disembarked from the ship and travelled to Houston for a further three weeks’ quarantine.
Going through Customs
According to popular lore, when they got back to the USA, the three astronauts had to go through immigration and fill out customs forms. Not only that, but they had to declare their cargo too. As it turns out, no, this did not happen. The astronauts were not bogged down by any customs paperwork on their return.
Read more: Did Man Really Land on Moon? The Dilemma of Apollo 11’s Missing Tapes
The customs form on the U.S. Customs and Border Protection Service website is authentic, of course, but it was more of a practical joke than a requirement. The Customs Service’s District Director for Hawaii created it, and, although the form gives its filing location as Honolulu Airport, the astronauts signed it with an auto-pen at the NASA headquarters later that year. On the form, the three astronauts listed Cape Kennedy, Florida, as their starting point and mentioned that they visited the moon for a stopover. They also noted moon rocks and moon dust as their space cargo.

The customs-and-immigration form jokingly filled out by Apollo 11 astronauts. (NASA/U.S. Customs and Border Patrol)
Current requirements of astronauts
Currently, it is a regular process for astronauts to go through customs. Not to travel into space, but to reach the training and take-off destinations on Earth from where they can begin their space missions to the International Space Station. Space astronauts train, at present, in the USA, Canada, Europe, Russia, and Japan, and they have to through immigration during the routine flights back and forth.
For more unusual stories & intriguing news follow STSTW Media on Instagram and Facebook. Also, join our live chat discussion on Twitter.
Do you have a story/photo for us?
We welcome your contribution at [email protected]. Please include your name, city, state, and country.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Why the Apollo 11 Astronauts Went through Customs & Immigration after Entering Earth? appeared first on .
]]>The post Wan Hu- The First Astronaut Propelled Into Outer Space? appeared first on .
]]>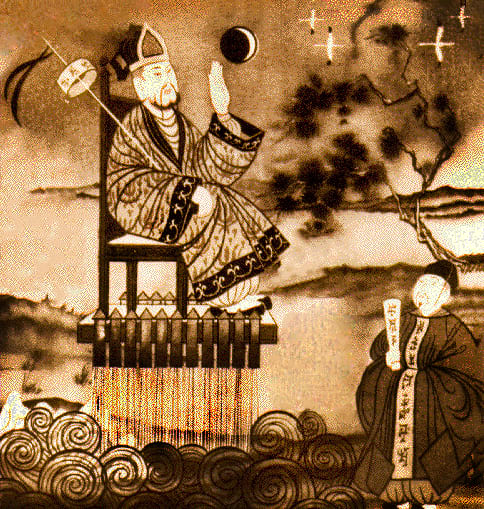
Artistic depiction of Wan Hu launching himself into space. (NASA)
It is said the roots of this endeavour began as early as 6000 years BC when ancient cultures were trying to understand the qualities of celestial objects. In China, in an area dominated now by the Gobi desert, Wan Hu put into practice a mission to get closer to the stars. So does this mean his mission to step into outer space was successful?
Read more: Dressmaker Who Jumped off the Eiffel Tower Experimenting with Self-Designed Parachute-Suit
Seeking the stars

Wan-Hoo crater, on the far side of the moon. (NASA)
An obsession with the stars and space is not a modern concept. It has been observed and studied since ancient times in various ancient empires. For example, since the 6th Century BCE in Ancient China astronomical observations were kept. An astronomer called Gan De made a star map as early as the 4th Century BCE. A few centuries later it is reported that Wan Hu looked to get closer than any person had to the sky. Some reports state he lived as early as 2000 BCE while others place him in the Ming Dynasty around the 16th Century ACE.
Wan Hu strapped himself to a bamboo chair with forty-seven gun-powder filled rockets, and a large kite system for movement and to act like a parachute when returning to the ground. Forty-seven assistants used torches to set light to the rockets, which propelled the wannabee astronaut upwards through a cloud of smoke and a massive explosion. It was said that the rockets exploded at various times, yet no remains were found of the chair or of Wan Hu.
Fact or fiction?
Wan Hu is revered in Chinese legend but most believe the story to be fake or allegory such is the ridiculousness and recklessness of the act. If it happened, then the success of even reaching the sky seems impossible. It seems he was a well-educated man, so it is more likely his experiment was a show. A famous US television program set up a recreation of the event to test the hypothesis,
“The television series Myth busters had attempted to recreate… Wan Hu’s flight by using materials which would have been available to him in an episode aired in 2004. In the experiment, the chair naturally exploded on the launch pad, and the crash test dummy showed what would have been… critical burns.”
Whether true or untrue, it becomes part of humanity’s journey to reach outer space. The reason being is that four thousand years later the dream became a reality,
“In 2003, Yang Liwei was launched aboard Shenzhou 5, becoming the first person sent into space by the Chinese space program.”
For more unusual stories & intriguing news follow STSTW Media on Instagram and Facebook. Also, join our live chat discussion on Twitter.
Do you have a story/photo for us?
We welcome your contribution at [email protected]. Please include your name, city, state, and country.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Wan Hu- The First Astronaut Propelled Into Outer Space? appeared first on .
]]>The post Trump Gives Green-Light for Moon-Mining: How Does it Affect Outer Space Politics? appeared first on .
]]>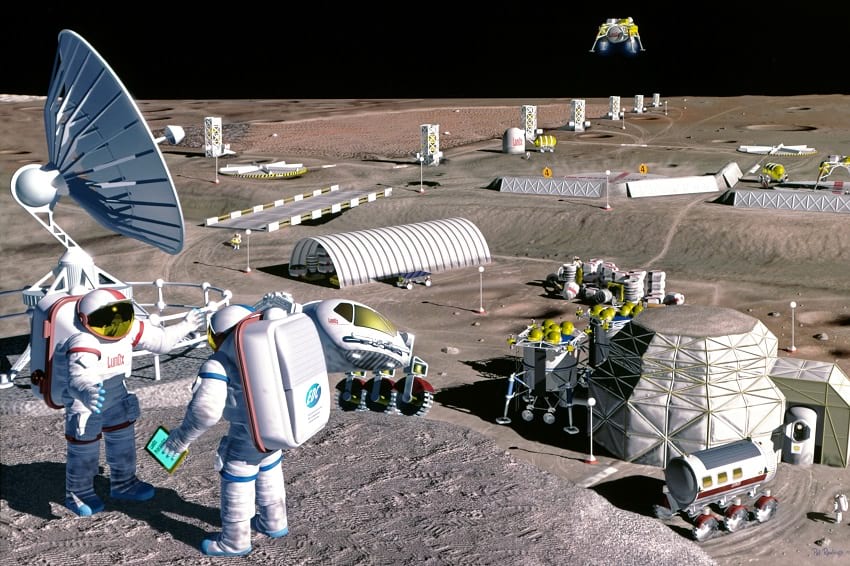
Artistic impression of a future moon colony. (NASA / SAIC / Pat Rawlings)
Amidst the deadly Coronavirus pandemic that has struck the entire world, Donald Trump, the President of the U.S., signed an executive order on April 6 that has a far-reaching impact on international relations and outer space politics. The treaty asserts that the U.S. does not think of space as a “global commons”. Therefore, it shall allow the country to mine lunar resources without requiring an international treaty to permit it. The White House believes that the water, ice and other lunar resources are available for the taking for the country of United States, which will help them in the establishment and consolidation of human presence on the moon.
Benefits of space mining
Sarah Cruddas, a space journalist, believes that mining the Moon would be rather beneficial and will aid humans to go further into space, like Mars, for instance. She also said that the Moon could operate as “an intergalactic petrol station” since it has resources essential for rocket fuel–hydrogen and oxygen. If there was a petrol station in space itself, it would mean that rockets could travel further in space as fuel limitations would no longer be a concern. Cruddas simplifies this idea with an analogy saying,
“It’s like not taking a kitchen sink when you go on holiday. We shouldn’t need to take everything with us when we go into space”.
According to Benjamin Sovacool, a professor of energy policy at the University of Sussex, humankind is aggressively blowing a hole through the resources at our disposal. Professor Sovacool believes that mining on the moon for resources could help in the building of things like electric cars, which would be beneficial in protecting the environment for the long haul. However, he also reiterates that space mining does not provide any short-term solutions in dealing with climate change.
The moon treaty of 1979
The ‘1979 Agreement Governing the Activities of States on the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies’, more commonly referred to as the ‘Moon Treaty of 1979’, stipulates that nations may not mine resources in outer space. However, several space-faring countries of the world including the U.S do not recognise the treaty. Countries that are already engaged in spaceflights or intend to do so have not adopted the Moon Treaty.
In fact, earlier in 1967 a treaty was signed called the ‘1967 Outer Space Treaty’, according to which, the use of lunar resources was allowed. Also, in 2015, Congress passed a law according to which American companies and citizens would be allowed to use moon and asteroid resources.
Though it was agreed that any nation can not claim the moon as their property, but currently it quite resembles maritime laws. Sarah Cruddas says, “If you go there, find it and mine it – it’s yours to keep.”Professor Sovacool explains that the typical argument for space settlement is that it will be our only escape since we will eventually ruin Earth’s ecosystem beyond repair. It is a viewpoint that asserts that the sole way to preserve a future for mankind is by seriously considering space settlement.
What does Trump’s executive order entail?
According to the executive order signed by President Trump, it is made clear that the U.S not only does not see space as a “global commons”, but it also makes things very official. According to administrative sources, the executive order was underway for nearly a year. The order also states that there are commercial partners taking part in an “innovative and sustainable program” which is being led by the U.S in order to “lead the return of humans to the Moon for long-term exploration and utilization.” The treaty states that a logical extension of this plan is to carry out human missions to Mars and other destinations in the long run.
In 2018, NASA, the space agency of the United States, had announced their plans to send astronauts to the moon by 2024, which had last been attempted in1972. NASA’s program for crewed space exploration, also known as ‘Artemis’ plans to send two of their astronauts to the moon by 2024 and aims to “establish a sustainable human presence on and around Earth’s nearest neighbour by 2028”. According to NASA officials, lunar resources, especially the water ice which is said to be found abundantly on the floors of the polar craters, is probably the doorway to the beginning of Artemis’ huge ambitions.
Scott Pace, who is the deputy assistant to Trump, along with being the Executive Secretary of the U.S National Space Council, said: “This executive order establishes U.S. policy toward the recovery and use of space resources, such as water and certain minerals, in order to encourage the commercial development of space.”
Dissenting views and a space race
The U.S has received many dissenting views, one of which belongs to the Russian space agency ‘Roscosmos’ which has condemned the executive order and labelled it colonialism. The deputy director-general of Roscosmos, Sergey Saviliev said, on the matter of international cooperation, “Attempts to expropriate outer space and aggressive plans to actually seize territories of other planets hardly set the countries (on course for) fruitful cooperation.” He proceeded to liken it to and remind us of the impact of British Colonialism specifically, and Colonialism as a concept, and how it has gone down in the annals of history.
However, despite criticising the U.S for its move about mining on the moon, Russia is not too far behind. They have expressed their plans to hopefully establish a permanent base on the moon sometime after 2025 in order to extract Helium.
China too has similar plans as Russia and the U.S with regard to asteroid mining and space explorations. In fact, there are talks that China and Russia may even team up in order to establish a “joint lunar and deep space data centre with hubs in both the countries”.
The ESA, or European Space Agency, has also expressed explicit interest in moon mining.
Trump’s space mission in a nutshell
Trump’s lunar development plans rely heavily on the cooperation between the private sectors and the U.S. Government. The signing of this latest executive order by Donald Trump will quite possibly not only strengthen the position of the U.S on an economical front but also in terms of their military strength. This aggressive encouragement for the activity of moon mining given by Trump may be considered a result of his presidential pursuits. He has consistently shown a very active interest in outer space over the years. He has endeavoured to lift regulations that hindered several mining projects which were given under the presidential rule of Barack Obama. In 2019, the United States became the only country to have an independent space force, cementing the nation’s position as a forerunner in the space race.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “A Glimpse into the Exciting World of Space Tourism“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Trump Gives Green-Light for Moon-Mining: How Does it Affect Outer Space Politics? appeared first on .
]]>The post Stanford Torus & Bernal Sphere: Model Space Colonies for Mankind to Set up Base in Space appeared first on .
]]>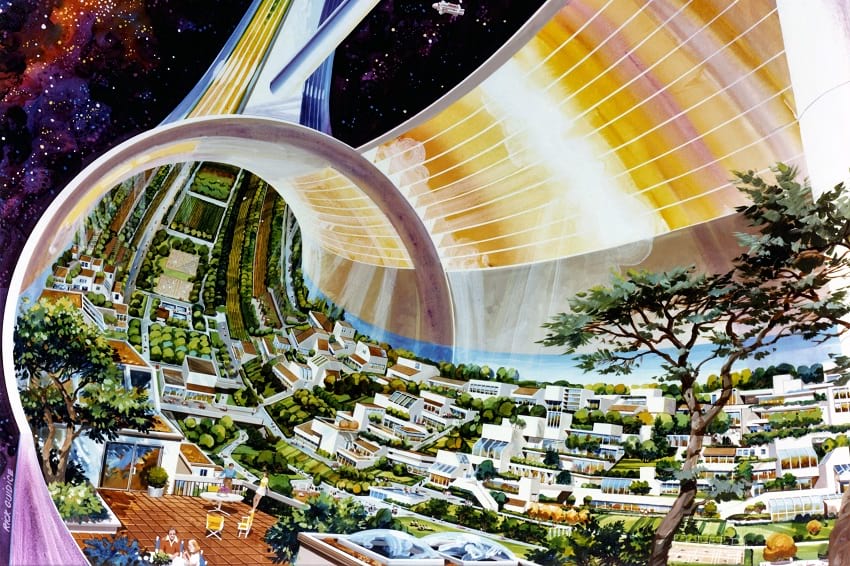
Space colony concepts from the ’70s. (NASA)
A NASA backed study that took place in 1975 gave rise to two space colony form factors- the Bernal Sphere, and the O’Neill Cylinders. A third concept also arose from the same study which was an amalgamation of the first two space colonies to form a doughnut-shaped ring in structure. This concept is known as Stanford Torus, which derives its name from Stanford University where the research was conducted during the 1975 NASA Summer Study. “Torus” in Greek or Latin stands for ‘doughnut’ or ‘bagel’.
A background to space colonization
In 1869, Edward Everett Hale wrote and published “The Brick Moon”, a story about a satellite made of bricks which are sent into space. Though it exists only for navigation reasons, it actually accidentally brings people aboard. After several trials and tribulations, the characters realize that they were in a space station. This was one of the earliest depictions of space travel and a space colony. Space travel has captured our imagination since the dawn of our civilization. From wanting to visit the mighty Gods who ‘live in the heavens’, to the modern desire to go to the moon, it has always been a significant part of literature. But space colonization, in itself, is a very modern concept.
Authors like Robert A. Heinlein and Issac Asimov, and scientists such as Carl Sagan, have all advocated for a unified effort to conquer the stars. Much of the modern idea of space colonialism was first postulated and then published in the year 1975. Stanford University and NASA Space Camp did collaborative research, speculating the future of Space Stations as postulated in Space Settlements: A Design Study. Over nineteen professors across various fields and a few student-volunteers got together for a 10-week program to construct a fairly accurate picture of how humans can, on a large scale, establish their habitat in space.
Stanford Torus
Proposed by NASA, The Stanford Torus is a doughnut-shaped ring that is one mile in diameter and is designed to house over 10,000 people in space. It is designed to be a self-sufficient colony, completely capable of producing food, support manufacturing and enable residential capabilities akin to that on Earth.
The Stanford Torus would rotate at the speed of 1 revolution per minute just to produce a weak artificial gravity. It would require a highly reflective mirror, angled at 45 degrees, to provide sunlight to generate electricity and for agriculture. The estimated energy requirements have been calculated to be as high as 18 kW per person.

An artistic depiction of a Stanford torus’s exterior. (Don Davis / NASA)
Manufacturing the Torus would be a challenge in itself. Since the mass would probably weigh over 10 million tonnes, how would one expect to extract that amount of materials from Earth? The answer is simple: the moon. Futurists predict that the materials would be extracted from our moon, considering that the moon is rich in materials such as aluminium. They also suggested that humans could also smelt those materials through the power of the sun, i.e. solar furnaces. This is a viable option since the sun would be a simple, efficient and nearly limitless source of fuel.
The colony would also need to generate a lot of heat. To provide for that, radiators as large as 900,000m2 would be installed, to generate heat as hot as 280 K. The ring is also connected to a hub via a number of “spokes”, which serve as conduits for people and materials travelling to the hub.
The interior space of the Torus would be used for residential areas, shaped into large “Valleys” having Earth-like features. The Torus would probably look like a long and narrow glacial valley with its residential complex resembling “a bustling suburb”.
Bernal Sphere
The Bernal Sphere was first proposed by an Irish scientist named John Desmond Bernal, through his book ‘The World, the Flesh, & the Devil’ in 1929. There he talks about the future of humankind and its future habitat in space. In his original design, he had imagined a non-rotating shell, 16 km in diameter, capable of holding a population of around 20,000-30,000 people.

An artistic depiction of a Bernal sphere’s exterior. (Rick Guidice / NASA)

The internal view of a Bernal sphere. (Rick Guidice / NASA)
However, the modern conception of the Bernal Sphere comes from Gerard K. O’Neill (who was the technical director in the Stanford-NASA collaboration camp). O’Neill had further expanded on the hypothetical settlement, originally conceived by Bernard, in his book “The High Frontier: Human Colonies in Space”.
O’Neill imagines our sphere into two incarnations:
–Island One: In its first incarnation, Island One, the diameter was decreased to 500m and the shell rotated at 1.6 RPM to produce complete artificial gravity. O’Neill also envisioned that his structure would support populations up to 10,000 people and would have a dedicated agriculture section called “the Crystal Palace”. Like the Torus, it would also use external mirrors to reflect sunlight for both electricity and farming. O’ Neill’s choice of the sphere was aimed towards resolving air pressure and radiation-related issues.
–Island Two: A larger incarnation, Island Two, was to have a spherical diameter over 1.8 km. This Island is, however, designed as a manufacturing space: emphasising less on housing and more on industrial production.
Can space colonies soon be our reality?
There are a lot of problems with the design of either of the two settlements, the Stanford Torus and the Bernal Sphere. The first drawback is the energy requirements. We certainly cannot use exhaustible forms of energy such as fossil fuels as a primary source of energy for these projects. At the same time, secondary renewable sources of energy, such as solar energy, have very low efficiency (as low as 22%). There is also a larger problem: most of the materials involved are required in humongous quantities, and would be impossible to extract from Earth, itself. Even with suggestions such as extracting materials from Mars or Saturn’s moons, the sheer costs of transportation itself would be backbreaking.
One of the potential solutions to this problem is to invest in Green Energy as much as possible. Improving technologies such as solar energy would help us in the long run. Renewable resources could be a really reliable source of energy in the vast emptiness of space.
Arthur C. Clarke once said that ideas pass through three stages:
STEP 1: “Impossible”
STEP 2: “Possible, but not really sustainable in the long run”
STEP 3: “It was a great idea all along.”
The reality of space travel and habitation, however, depends on the economics of the future. If history is the true predictor of the future, then the possibilities are not that far off the mark.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “A Glimpse into the Exciting World of Space Tourism“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Stanford Torus & Bernal Sphere: Model Space Colonies for Mankind to Set up Base in Space appeared first on .
]]>The post Lost Cosmonauts of USSR: Did the Soviet Union Cover up its Secret Cosmonaut Casualties? appeared first on .
]]>
Lost Cosmonauts: Soviet cosmonaut Alexey Leonov during the spacewalk, 1965. (Ria Novosti / Science Photo Library)
Today, we realise that USSR’s Yuri Gagarin was the first man to journey into outer space and USA’s Neil Armstrong was the first to set foot on the Moon. However, there are many conspiracy theorists, keep refuting the claims and call these events as a hoax.
Space travels have always come at a great cost, post-WW-II when the Cold War between the Soviet Union and USA was at its peak, both countries were trying their best to be one up on the other in the space race. It is said that during this period there were certain secret Soviet space programs that had gone awry, with cosmonauts never making it back, to either their country or planet.
There are also many conspiracy theories that corroborate the fact that the Soviets had sent cosmonauts in space prior to Gagarin, but they were considered either lost or dead while reentering into the Earth’s atmosphere. It is said that to avoid bad publicity and not lose the space race, the USSR covered up the failed events.
Cosmonaut Ivan Ivanovich
Interestingly, one name that stands out in the list of lost cosmonauts is Ivan Ivanovich, which had fueled the world’s interest in space flights. In March of 1961, the Soviets sent a test flight into outer space with Ivan Ivanovich aboard, along with some reptiles and critters. The manned test flight returned successfully, but when media covered the entire event and spotted the lifeless body of the cosmonaut inside, they began speculating that the Soviet mission had ended in tragedy.
Ivan Ivanovich was in fact, a life-like mannequin placed inside the flight to test whether it could be a success for future programs. Ivan was sent in space again a week later, which set the stage for Gagarin’s grand spaceflight – Vostok 1 – giving USSR an edge over her competitors.

Full body display of Ivan Ivanovich at the National Air and Space Museum. (Eric Long / Smithsonian Institution)
Was Vladimir Ilyushin the first man in space?
Apart from these lost cosmonaut theories, there was one theory, which particularly drew the world’s attention. Vladimir Ilyushin, a test pilot and later Soviet general, was the constant subject of a conspiracy theory, which stated that he was the first man in space rather than Yuri Gagarin. While USA was racing against the USSR to launch their first vehicle in space in the 1960s, it was alleged that Soviets had already sent Ilyushin into space a week before Gagarin. His spaceflight had steered off course and landed in China, where he was held as a prisoner for a year, before being sent back to USSR. It was later assumed that his death in a car crash was only the Soviet Union’s way of covering up the failed launch.
Judica-Cordiglia brothers’ recordings
Among all these allegations, two Italian brothers known as Judica-Cordiglia brothers came forward with startling discoveries. In the late 50s, Achille and Giovanni Battista set up their experimental radio station with homemade equipment on an abandoned German bunker. It had all the necessary listening equipment, which they claimed had picked up radio frequencies from several space missions, which were secretly being carried out by the Soviet Union.
They called the site Torre Bert, from where they started to eavesdrop into the frequencies of the secret Soviet space missions. The twosome claimed to have picked up conversations between the cosmonauts and ground stations that lasted for a few seconds as the space shuttles passed over their city.

The Judica-Cordiglia brothers. (Wikimedia Commons)
As their makeshift radio station grew, the brothers hired more amateur space enthusiasts, who helped them in their endeavour to dig deeper into Soviet Union’s dark secrets. They claimed to have come up with as many as nine recordings, which picked up disaster signals and cosmonauts crying out for help as they re-entered into the Earth’s atmosphere.
Most of the recordings were of labored breathing of cosmonauts, an astronaut dying due to heart failure on one occasion and at one time, a cryptic message had been sent to the ground station. They also claimed to have heard distress signals from astronauts, whose existence was never reported by the Soviets. The brothers’ recordings were more than enough to prove that the Soviet Union had failed miserably in their space venture, resulting in casualties and losing their cosmonauts.
While The US hailed the efforts of the Italian brothers, the USSR rubbished their claims, for they could have possibly brought the country’s space malfunctioning to the fore.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “The Soyuz 11 Tragedy – The Death of Three Soviet Cosmonauts in Space“.
Recommended Read:
Starman: The Truth Behind the Legend of Yuri Gagarin | By Piers Bizony
Recommended Visit:
National Air and Space Museum | Washington, D.C., United States of America
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Lost Cosmonauts of USSR: Did the Soviet Union Cover up its Secret Cosmonaut Casualties? appeared first on .
]]>The post Why Were the Apollo 11 Astronauts Quarantined after Returning from the Moon? appeared first on .
]]>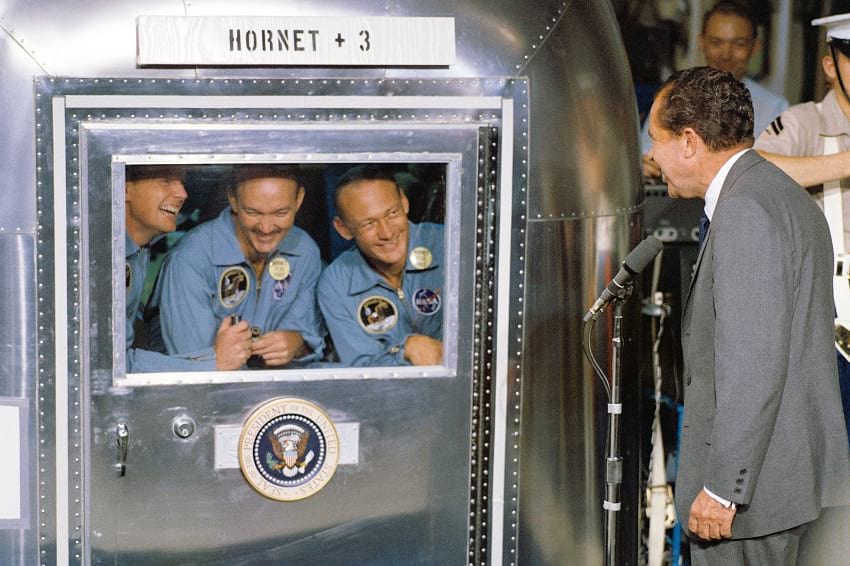
President Richard Nixon welcoming the Apollo 11 astronauts while they are quarantined. (GPA Photo Archive / Flickr)
The Cold War was a tense political stalemate that lasted for many years, affecting the lives of millions of people all over the world. The Space Race was a significant element of the Cold War. It was an uncompromising competition played out by the USA and the USSR. In the beginning, the USSR was successful in a lot of space-related achievements. The Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human ever to go into space. However, the United States grabbed an enormous advantage on July 20, 1969 when they successfully managed to send astronauts to the moon as part of the Apollo 11 mission.
The Apollo 11 mission
Pre-launch
On July 16, 1969, the Apollo 11 mission was launched from Kennedy Space Center in Florida with the help of a Saturn V rocket. Apollo 11 was the fifth crewed mission of NASA’s ambitious Apollo program. The Apollo 11 spacecraft could be divided into three important parts – the command module (CM), the lunar module (LM) and the service module (SM). The CM had a cabin where the three astronauts would reside and it is the only part which returned to earth. The SM provided the CM and LM with electrical power, propulsion, oxygen and water. This was achieved with the help of revolutionary hydrogen fuel cells. The lunar module (LM) had two stages – one for descent onto the lunar surface and the other for an ascent stage back into the lunar orbit. The crew consisted of Neil Armstrong, Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin, and Michael Collins.
Launch
The launch was viewed by at least a million spectators from the highways and beaches close to Merritt Island. Many dignitaries were present at the launch, including former president Lyndon Johnson and his wife Lady Bird Johnson. On July 19, the Apollo 11 spacecraft passed by the moon and fired its propulsion systems and entered lunar orbit. The Sea of Tranquillity was selected as the landing zone because earlier surveys had established the place as relatively flat and smooth.
Moon landing
The lunar module landed on the lunar surface at 20:17:40 UTC. Consequently, the Apollo 11 mission allowed human beings to set foot on the moon for the first time- with astronaut Neil Armstrong making history as the first man on the moon, soon followed by astronaut Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin.
Ascent into lunar orbit
The lunar module made its ascent and rendezvous with the CM on 21st July 1969.
Apollo 11 Quarantine
After splashdown
The USS Hornet, a US Navy aircraft carrier was selected as the primary recovery and rescue ship for the Apollo 11 mission. The Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) was also placed on-board of the recovery ship. At the time, NASA did not know for sure that the conditions on the moon were completely sterile. They considered that there was a chance of the Apollo astronauts bringing back alien pathogens with them from the moon. For this reason, NASA extracted the astronauts and immediately placed them in Biological Isolation Garments (BIGs). Then, they were placed in a life raft.

Apollo 11 crew wearing biological isolation garments while being rescued. (NASA)
In the life raft, the three astronauts were rubbed with sodium hypochlorite (bleach). The Columbia was rubbed down with Betadine so as to remove even the faintest traces of lunar dust. The astronauts were subsequently transported by helicopter to the USS Hornet, which was lowered into the hangar bay via the ship’s elevator. The astronauts walked 30 feet to the MQF. They had to stay in their BIGs until they were safely situated within the MQF. For good measure, the life raft that carried the astronauts was also shot and drowned.

Apollo 11 astronauts exiting the recovery pick up helicopter to board the U.S.S. Hornet aircraft (NASA)

Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) being lowered from USS Hornet recovery ship. (NASA)
What is the Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF)?
The Mobile Quarantine Facility, or the MQF, is a repurposed airstream trailer which was used by NASA for quarantining astronauts returning from the Apollo missions. The astronauts would then begin the three-week process of earth-based quarantine. The MQF also housed an engineer who operated the entire trailer and an in-house physician. While the astronauts were in the MQF aboard the USS Hornet, they were visited by President Nixon. The astronauts were also visited by their wives while they were in the MQF.
After Nixon departed, the Columbia (CM) was lifted by crane and placed next to the MQF. They were both connected by a flexible tunnel so that the astronauts could retrieve the lunar samples, data tapes and photographic film. When the Hornet returned to Pearl Harbour, the entire MQF was airlifted to the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) situated at the Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas.
The Extra-Terrestrial Exposure (ETE) law
The Extra-Terrestrial Exposure Law was the popular name for the set of official regulations adopted by NASA during 1969-1977. As scientists did not exactly know that space and the moon were completely sterile, they did not want the astronauts to bring back any dangerous pathogens. According to this law, the 21-day quarantine process of all moonbound astronauts was made mandatory. In 1977, it was proved beyond any doubt that the moon was completely sterile and NASA removed the Extra-Terrestrial Exposure Law from its set of regulations. Following this, the US Government also removed this law from its federal regulations.
Reason for revocation of the ETE law
The lunar samples brought back during the Apollo 11 mission were analysed thoroughly by scientists at NASA. After extensive testing, it was established without any doubt that the moon was completely sterile and there were no life forms of any kind residing in the lunar samples. The entire reason for the quarantine of the Apollo 11 astronauts was to prevent the spread of “space germs”. Although it can seem preposterous now, it was a necessary precaution that had to be taken for the safety of everyone else.
All three astronauts rode in ticker-tape parades organised in their honour in New York and Chicago on August 13, 1969. On the same day, there was a State Dinner organised in their honour which was attended by members of Congress, foreign dignitaries and important US politicians at the Century Plaza Hotel at Los Angeles. President Richard Nixon and Vice-President Spiro Agnew presented all the three astronauts with the Presidential Medal of Freedom.

Apollo 11 ticker tape parade. (NASA / Bill Taub)
Putting humans on the moon is one of the most significant scientific achievements of the 20th century and it is awe-inspiring. It is also a remarkable endeavour, considering that humans had invented reliable flight technology only fifty years ago.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected]
RELATED
The post Why Were the Apollo 11 Astronauts Quarantined after Returning from the Moon? appeared first on .
]]>The post ʻOumuamua: A Mysterious Interstellar Rock Discovered in Our Solar System appeared first on .
]]>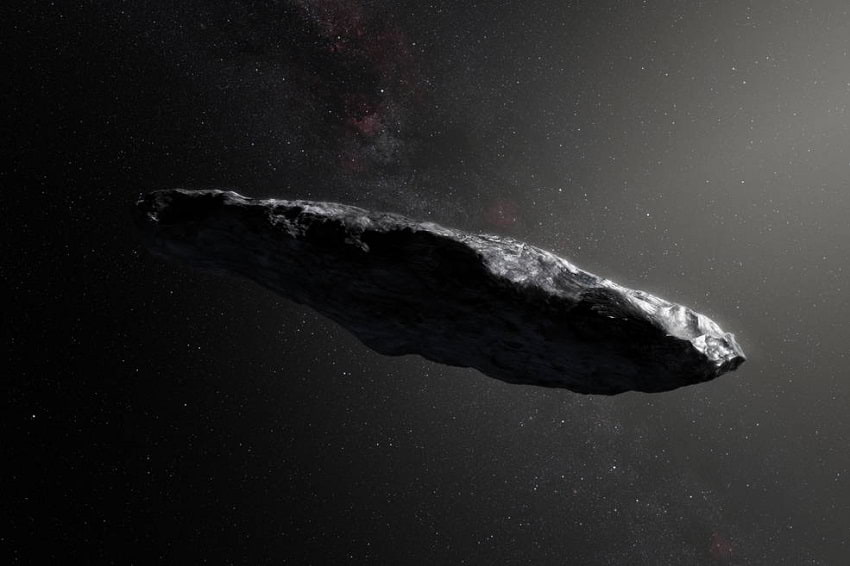
An artistic impression of ‘Oumuamua. (European Southern Observatory / M. Kornmesser)
A mystery rock was spotted in our solar system on October 2017, which ended up sparking a lot of questions amongst the scientific community all over the world. This rock has been given the name ʻOumuamua – a Hawaiian word that basically stands for “scout or messenger from the distant past”. Prior to the detection of ʻOumuamua, we were unaware of the presence of any such interstellar objects present in our solar system.
The only feature that marked the rock as something that might belong to our solar system itself, was its composition of minerals and a characteristic reddish hue. Apart from these qualities, it appeared to be a space rock unlike anything ever spotted before. Shaped like a cigar, ʻOumuamua is nearly 400 meters in length. Not only that, the peculiar nature of the rock also includes the characteristic way it moves- spinning its way through space. Researchers say that it may be a ‘planetesimal fragment’, in the sense that during the formation of a planet in another solar system, it got ejected into space as a result of several factors which may include gravity and explosion of gases.
Discovery of the mystery rock
Observed from the Pan-STARRS1 telescope at the University of Hawaii, funded by NASA’s Near-Earth Object Observations program (NEOO), the ʻOumuamua was initially categorized as a comet. Later on, scientists decided it may be an asteroid due to the unusual activity exhibited by the space rock. Prior to this, interstellar objects were just a theory put forward by scientists. The arrival of the ʻOumuamua confirmed these theories that had plagued scientists for years. Observations made by researchers conclude that it is likely that the space rock has traversed its way through space for millions of years before finally entering our Solar System.
After the momentous discovery of the ʻOumuamua was made at the University of Hawaii, several telescopes were used to continue studying the interstellar object further. These included the European Organisation for Astronomical Research’s (ESO’s) Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile to measure its brightness, orbit and color. Space telescopes like the Hubble and Spitzer tracked the movement and speed of the interstellar object. The speed of the ʻOumuamua was marked as 98,400 mph (158,360 km/h) relative to the sun.
Peculiar characteristic traits of ʻOumuamua
With the help of images combined with ESO’s telescope and FORS instrument, a team of researchers, led by Karen Meech of Institute of Astronomy in Hawaii, discovered that the brightness factor of the space rock varies by 10 every 7.3 hours as it spins on its axis. This variation is a characteristic of the ʻOumuamua as a result of its peculiar size. The ratio of its length to width varies by a factor of 10 as well. The length to width ratio of typical space rocks tends to vary by 1:3. There is no evidence of any water or ice present on the surface of the rock, no dust present inside or around it, and it is a completely inert object right to its core.

ʻOumuamua’s changing brightness as it rotates. It appears the brightest when its full length is facing towards the Earth. (NASA / JPL-Caltech)
There are four classifications for a space rock with respect to its eccentricity. They could be circular, elliptical, parabolic, or hyperbolic. The ʻOumuamua happens to have a hyperbolic eccentricity. It was observed that most rocks having hyperbolic eccentricities have values greater than 1- typically around 1.0001. Astonishingly, the ʻOumuamua had a measured eccentricity of 1.2.
ʻOumuamua: An alien probe?
The space rock exhibited, interestingly, added acceleration as it reached deeper into our Solar System. Due to this occurrence, the ʻOumuamua was almost classified as an alien probe, being controlled by organisms that were from beyond our known world. However, data indicated that there was no such possibility, since there was no sign of activity on the rock itself. Also, owing to the sheer speed by which it travelled through space, it would be nearly impossible for any organism to exist on it. There was still speculation amongst certain scientific and extra-terrestrial enthusiasts’ fraternities as the extremities an alien organism may survive our beyond what we have been able to ascertain as definite.
The mystery behind the ʻOumuamua’s change in trajectory
Slight deviations noticed in the path of the space rock are not just an effect of gravitational forces, but could also be due to loss in mass. The thrust could have occurred due to the heating up of the surface, which would eventually lead to the formation of a comet tail comprised of several gases. As this did not actually occur, it ended up puzzling scientists till they realized that the Oumuaumua was actually inert in nature. Not only that, there are several other factors, including the rotation period, that come into play.
In the case of loss in mass and formation of a cometary tail, the rotation period around its axis would have varied. Fragmentation of the rock would have caused an abrupt kick in speed, but that did not happen either. Authors Shmuel Bialy and Abraham Loeb suggest that the change in trajectory could be due to solar radiation pressure.
Study of space rocks
Further study of the interstellar rock was declared impossible, due to the lack of adequate technology. No rockets made by humans would be able to catch up with the Oumuaumua. The gravitational net between Jupiter and the Sun hold the possibility to trap interstellar objects entering our Solar System in the future, but this is just a theoretical speculation at the moment.
ʻOumuamua 2.0
Looking forward, the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope will be operational by 2020-2022, and make the study of space rocks much easier.
On August 30th, 2019, Gennady Borisov detected another interstellar object that appeared to be something we might call the ʻOumuamua 2.0. As observed by NASA’s Scout system, it appears to have an unusual orbit, and measurements taken by compiling data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope classify the object as an interstellar space rock. Its closest approach would be in the month of December.
Assumptions have been made regarding the trajectory and traits of this rock, and it is under constant observation. Whether a cometary tail will appear, or not, in the course of its path is the question. Bumps in speed have also been kept a look-out for, to confirm the interstellar nature of the rock. If there is no out-gassing, no tail, and no explanation regarding its origin, the nature of the ʻOumuamua 2.0 will be confirmed, and will aid in our study of the increasingly frequent detections of interstellar objects.
Enjoyed this article? You would also love “Truth Behind The Black Knight Satellite Conspiracy Theory“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post ʻOumuamua: A Mysterious Interstellar Rock Discovered in Our Solar System appeared first on .
]]>The post Supervoid: A Giant Empty Region of ‘Nothingness’ in the Midst of Our Universe appeared first on .
]]>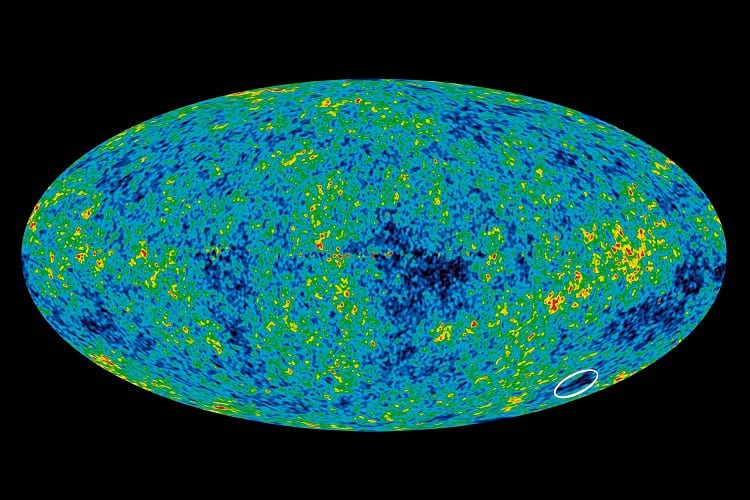
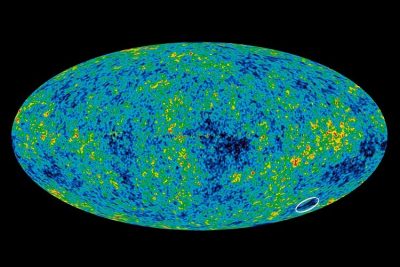
The circled area is the cold spot, suggesting the presence of a supervoid. (NASA)
From time immemorial there have been abundant discoveries and unsolved questions about the Universe. Starting from the revolutionary Big Bang Theory, to the recent images of black holes, humans, rather scientists, have made remarkable discoveries about the Universe. One of the lesser-known of such marvellous discoveries is perhaps the giant hole that our Universe harbours- the ‘Supervoid.’
The Supervoid is quite literally a giant comic hole in the Universe. It is a region that shrinks everything in and around it, but it lacks the standard features of a conventional black hole. A black hole is a region of space that is created by the curving of the continuum that joins space and time. This phenomenon is typically caused by some gigantic mass. The giant hole, on the other hand, is devoid of all kinds of matter.
An endless abyss
This hole is a giant void, devoid of stars, gas and other usual matter, including the darkness that envelopes the space all around us. “Not only has no one ever found a void this big, but we never even expected to find one this size,” says researcher Lawrence Rudnick of the University of Minnesota.
The hole is nearly 1.8 billion light years across. It is not uncommon to discover voids such as this in our vast Universe- the size of this particular hole, however, is unprecedented. “Supervoids are not entirely empty, they’re under-dense,” stated András Kovács, who is a co-author at the Eötvös Loránd University in Budapest. A very important and characteristic feature of this void is its temperature. As astronomer Carlos Frenk says, “It’s like the Everest of voids.”
Cosmic Microwave Background or CMB can track radiation back to the birth of our Universe. This supervoid can be spotted on the maps of CMB as discovered by NASA’s Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) in 2004. This observation was later confirmed by ESA’s Planck Satellite. Recently, the Institute for Astronomy at The University of Hawaii has found evidence stating that the density of galaxies in the supervoid is actually much lower than that in the rest of the Universe.
The universe: A perforated ball of cheese
Professor Carlos Frenk, a cosmologist at the University of Durham, acknowledges that the discovery of the “Cold Spot”, as it was dubbed, had raised quite a few eyebrows. The main reason for this- the theories around it all posed a direct challenge to orthodoxy, negating some suppositions made by The Big Bang Theory. However, it was inevitable to go down the rabbit hole and research extensively to find the cause of the ‘cold spots’ and ‘supervoids’.
The Universe is, in fact, dispersed with holes and voids that are nothing but empty spaces, devoid of matter and gravitational pull. Consequently, when a particle of light (a photon) enters this void, it loses its energy but quickly regains some of it on exiting this hole. It is a known fact that the Universe is constantly expanding and changing. It is automatically presupposed that the exiting photon emerges into a medium that is less dense than what it was in when initially entering the void. Hence, the gravitational pull on the photon is a lot less than it was previously.
The photon converts its kinetic energy into a potential gravitational pull as it travels into the centre of the void. In a stationary Universe, the photon is ideally supposed to remain unchanged. But since the Universe is constantly stretching, the photon can no longer regain its original energy or the energy possessed by the other light particles in the Universe. This results in an overall drop in temperature. That is how the “cold spot” within the supervoids come to be. The exiting light from the void has a longer wavelength corresponding to the drop in temperature.
Two sets of data were used and compared to make this discovery. The scientists tested the objects that were found at infrared wavelengths by NASA’s Wide Field Survey Explorer (WISE). These were compared against the colours in visible light measured with the help of the robotic telescope Pan-STARRS1. They made a tomographic map of the galaxies that are present within the cold spot. The sudden drop in the number of galaxies led to the discovery of a region in the Universe that existed when the Universe was 11.1 billion years old.
Supervoid: A hole in the universe
Investigations around the phenomenon of supervoids, particularly this gigantic hole, are ongoing leading to new observations and new questions by the day. The biggest and most important of these issues that have come up is undoubted whether this Supervoid is a rare occurrence, or if there are more such voids out there. The discovery of other similar supervoids will help answer one of the biggest mysteries here- the relationship of the cold spots to the voids. As Dr Roberto Trotta, a cosmologist at Imperial College London said, “Now we have to figure out how does the void itself form. It’s still a rare event.” When scientists from the University of Minnesota discovered this massive hole in the Universe, they termed it as a “supervoid” with regards to the enormous size of it. This was then published in 2007 in The Astrophysical Journal.
Therefore, the Supervoid is simply an area with a lesser matter in comparison to the rest of the Universe. It is an accidental discovery as one might say, with due credits to NASA. There were investigating the spread of radiation as a result of the Big Bang due to the absence of about ten thousand galaxies when they stumbled upon this. Other voids in the Universe have thence made their appearance but none of them amounts to anywhere close to the size of the Supervoid.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Gliese 581g: A Habitable Exoplanet or Just Another Celestial Object Orbiting a Star?“
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
 Recommended Read:
Recommended Read:
Atlas of Astronomical Discoveries | By Govert Schilling
Genre:
Non-fiction > Space
RELATED
The post Supervoid: A Giant Empty Region of ‘Nothingness’ in the Midst of Our Universe appeared first on .
]]>The post Ham – The Chimpanzee that Paved Way for Launch of Manned Spacecrafts appeared first on .
]]>
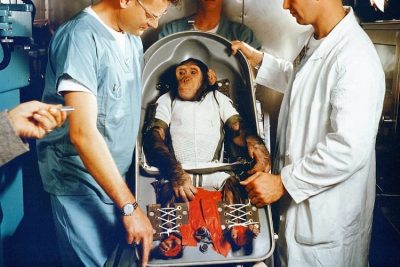
Ham – the chimpanzee in his biopack couch preparing for the sub-orbital spaceflight. (NASA)
The cold war between America and the Soviet Union (present-day Russia) wasn’t limited to just sea and territorial region. It extended well into space. In the Space Race, Russia took the lead by launching an artificial satellite Sputnik-1 into earth’s orbit in 1957. Later the same year Sputnik-2 was launched with Laika the canine cosmonaut who became the first animal to go into orbit. America in the meanwhile sent fruit flies (1947) and monkey-mice team (1951) into space. Life could survive in space; this was proved beyond doubt. But could life also perform a designated task in space? America sought an answer by sending Ham – the chimpanzee, into space and the answer was ‘yes’. The answer came full 10 weeks ahead of Soviet Astronaut Yuri Gagarin orbiting around the earth on 12th April 1961.
Ham – the chimpanzee was procured and trained for the space mission
Born in African forests of French Cameroons in 1957, Ham was procured and purchased for Holloman Air Force Base, New Mexico, America. It was one in a team of 40 chimpanzees chosen for training at the ‘School for Space Chimps’. The training was a part of NASA’s Project Mercury, which aimed at sending a human being in the space. On Jan 2, 1961, six from these 40 were shortlisted and shifted to Cape Canaveral, Florida for the last round of preparations. They were divided into 2 groups of 3 each, lest illness of anyone spread the infection to all six. The mission would help scientist understand if the human body could perform well at high speed and zero-gravity conditions of space travel.
Trained for responding to coloured light in a preplanned manner
The training schedule established a healthy rapport between the primates and their handlers. The health of chimps was thoroughly monitored. Ham, initially called No. 65, was supervised by a Neuroscientist.

Ham with his trainer at Cape Canaveral, Florida. (NASA on The Commons / Flickr)
The training was about testing a directed response to 3 lights – red, white and blue, kept before the chimps. Each light had a lever below it. The red light was continuously on, and its lever wasn’t supposed to be pulled. The white light was off and would flicker only when the related lever was pulled. The chimps were trained to switch on the white light once every 20 seconds. The blue light shone erratically for 5 seconds during which time the chimps must pull the lever related to blue light. Primates performing as per the directions were rewarded with food bite and water. Derelicts got punished with electric shock in the sole of their feet. Primates were also subjected to simulated microgravity and g-forces to acclimatize them with the space environment.
Ham the astrochimp had two other names before his return from the space mission

A technician displaying all the equipment of Ham the Astrochimp in preparation of the launch. (NASA on The Commons / Flickr)
Mercury Redstone 2 rocket was ready for take-off on 31st January 1961. Which primate would go on a mission was decided on 30th. The decision went in favour of the flamboyant Ham. Another primate (Minnie) was selected as standby. Interestingly, the name Ham was made public only after the successful return of the primate on earth. Before that, No. 65 was made his official name, and for a good reason. The officials felt that if a formal name was announced for the chimpanzee, it could add to bad publicity in case the primate couldn’t return safely from the space. Ham – the chimpanzee had a pet name too, ‘Chop Chop Chang’; that’s how the handlers addressed Ham during his training period.
Preparing for takeoff was elaborately planned

Ham in his spacesuit sitting inside MR-2 capsule prior to its test flight. (NASA)
Nineteen hours before takeoff, the selected primates were given a special diet and placed in their pressurized cabins with biosensors attached to their bodies. Seven and a half hours before takeoff, a chain of pre-launch examinations were conducted. Four hours before the journey, the two were dressed up in spacesuits, positioned in their couches, and taken to a transfer van. In the transfer van, they were provided with environmental control equipment. Two and a half hours before launch, only Ham was boarded into an elevator and ushered into the nosecone of the spacecraft. It would be a sub-orbital spaceflight as spacecraft wouldn’t orbit or circle the earth.
In spite of several problems, the mission was a success
Problems for the mission began right from the start. There was a dip in air pressure, but thanks to the buffer arrangement, Ham remained safe. A technical snag made spacecraft overshoot planned altitude of 115 miles and cover 157 miles. Speed too went on the excessive side. Against the planned speed of 44000 mph, the spacecraft reached a speed of 5,857 mph. Consequently, it landed on earth 422 miles away from the launch site, as against the planned distance of 290 miles. Naturally, salvage operations after the splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean got delayed. However, help reached in the nick of time and Ham escaped death-by-drowning.

Ham being greeted by the commander of the ship after his recovery. (NASA on The Commons / Flickr)
On return to earth, Ham was in high spirits and accepted apple given by the commander of the recovery ship. He also shook hands with the members of the receiving team. But for a little limp in legs, he was in a good physical shape. Flashing of cameras, and the commotion of the Press reporters did irritate him, and it took quite some time to cool him down.

Ham being rewarded with an apple after his successful spaceflight. (NASA)
Ham’s performance in space was on expected lines
Ham’s perform in the total 17 minutes of his journey in space was satisfactory. His reflexes to lights and levers were only a little slower in the space than on earth. Enough hint to the scientific community to go ahead with the manned spacecraft. As mentioned earlier, it was only after the success of the space mission that the name Ham was made public. Ham, the Astrochimp. Ham is the acronym for Holloman Aerospace Medical Center, the laboratory that trained the iconic primate. Coincidently, the-then lab commander was Lieutenant Colonel Hamilton ‘Ha’’ Blackshear.
In life, as well as death, Ham remained a subject of keen scientific exploration
Ham shot to instant fame and was widely covered in media. Till 1980, he lived at Smithsonian’s National Zoo at Washington DC. Then he was shifted to the North Carolina Zoological Park in Asheboro where he died in 1983. Skeleton from Ham – the chimpanzee’s dead body was removed and sent to the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology for studies and investigations. Other remains of the body were buried in Alamogordo, New Mexico, at the International Space Hall of Fame.
Several space programs followed in quick succession
Ham’s space jaunt opened the way for a chain of successful Mercury programs. Alan Shephard, the first American Astronaut was launched into space on May 1961. Enos, another chimpanzee, went into orbital space flight in November 1961 and made 2 full circles around the earth. In February 1962, John Glenn became the first American to orbit around the earth.
Was Ham the chimp subjected to cruelty?
The story doesn’t end here. There is a flip side to it, if a noted Primatologist, Dr. Jane Goodall is to be believed; she perused the photographs of Ham – the chimpanzee taken during 17 minutes of his space flight and after recovery of his capsule from the Atlantic Ocean. The photographs, according to her, were shockingly horrendous. Terror was writ large on the primate’s face. He lived alone in captivity for 20 years after travelling in space and died prematurely at the age of 25.
Goodall criticized NASA’s portrayal of Ham as a hero. Chimp’s pictures given in the media were selective and edited. The animal did go through bouts of extreme pain and distress but such pictures were kept away from the public. She also took exception to remove and exhibit the primate’s skeleton. That, she said, amounted to death-without-dignity.
The use of animals in experiments for the advancement of technology and human welfare will remain a grey area of human endeavour. Nevertheless, the contribution of Ham, the Astrochimp, will remain a milestone and a turning point in the history of Space Science.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Laika the Canine Cosmonaut – From the Streets to the Stars“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
 Recommended Read:
Recommended Read:
Animals in Space: From Research Rockets to the Space Shuttle | By Colin Burgess & Chris Dubbs
Genre:
Non-fiction > Space
RELATED
The post Ham – The Chimpanzee that Paved Way for Launch of Manned Spacecrafts appeared first on .
]]>The post Pale Blue Dot: The Iconic Photograph Showing How Microscopic But Brilliant Earth Is appeared first on .
]]>The blank space
13.8 billion years ago the Universe was created with a massive Big Bang, and over time Space itself has expanded. Gravitational forces have worked their magic, and the Universe has evolved into its present state. Our planet Earth is in the third position from the Sun, and together with her seven other siblings, forms the solar system. It is important to remember, our solar system is actually just one of the many solar systems in our Milky Way. And the Milky Way in turn, is just one of the innumerable galaxies in the Universe. Astronomers and cosmologists have been on a quest to unravel the eternal mystery presented by Space, since time immemorial. With the advent of modern technology, humankind has made remarkable leaps of success in this regard.
The Pale Blue Dot
Twenty-nine years ago, on 14th February 1990, Voyager 1 spacecraft clicked the first-ever picture of our solar system. Including Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter, Earth and Venus, the spacecraft ended up clicking a “family portrait” while turning the spaceship towards the Earth. This was not at all pre-planned. There had been, in fact, a total of 60 frames that the Spaceship had tried to capture, the ‘Pale Blue Dot’ being one of them.
Unfortunately, Mars had little sunlight, Mercury was very close to the sun, and Pluto turned out too dim while the picture was taken. Consequently, they are not visible in the iconic photograph. The picture was taken from a distance of more than 4 billion miles from Earth, at about 32 degrees from the ecliptic. The Earth looks like a mere point of light due to the huge distance between the Planet and the Spaceship.
Coincidentally, Earth lies right at the centre of the scattered light rays, thus resulting from the intense sunlight and the dramatic effect overall. It is one of the most famous photographs of the Earth, although it just appears as a ‘pale blue dot’ that is moving.

Earth as ‘Pale Blue Dot’. (Voyager 1 / NASA)
What is Voyager 1?
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched Voyager 1, a 722 kg robotic spacecraft on a mission to go into outer space and explore it in, way back in 1977. Voyager 1 was the first spaceship that was able to provide comprehensive images of the two largest planets, (Jupiter and Saturn) and their major moons. This space shuttle is still loitering in the Universe, and it is the first man-made shuttle to leave the solar system and explore beyond. It still receives command and transmits back important data back to the NASA Deep Space Network. When the spacecraft encountered Saturn in 1980, Carl Sagan proposed the idea of the spaceship to take one last picture of the Earth. Although the photograph would not be of much worth to science due to the lack of proximity, it would be meaningful as a perspective on our home in the Universe.
Why so blue?
From outer space, our planet Earth appears to be a blue due to the scattering of the Sunlight in its atmosphere. The wavelength of the blue colour is quite short and scatters to a great extent. This is the same reason why the sky appears blue when we look up from our planet as well! Another factor adding to the blueness of Earth is its huge oceans which also appear blue. From Space, the colour of the planet appears like a ‘pale blue dot’, as opposed to a dark blue one owing to the white light reflected by the clouds combining with the scattered blue light.
Pale Blue Dot by Carl Sagan
The sensation that this picture created is both unusual and difficult to put into words. A book named ‘Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space’ was written by Carl Sagan in 1994. In it, he says,
“Look again at the dot. That’s here. That’s home. On it everyone you love, everyone you know, everyone you heard of, every human being who ever was lived out their lives. Every aggregate of our joy and suffering is, thousands of confident religions, ideologies and economic doctrines, every Hero and coward, every creator and destroyer of civilization, every mother, father, hopeful child, inventor and explorer, every teacher of morals, every corrupt politician, every saint and sinner in the history of our species lived here—on a mote of dust suspended in a sunbeam.”
The image of the pale blue dot gives us a perspective of just how insignificant our lives on Earth are when compared to the vast majestic spread of the Cosmos. We think we are very safe here, in our big blue planet, but it is not so. The mundane things of life, ideologies like racism, sexism, imperialism, war and even emotional turmoil are just petty things. They are just momentary glorification of a fraction of a dot. Everything will collapse into ashes if there is a slight distraction in the orbital path of any large heavenly body, and it collides with us. Yet, living in this distinct planet that benefits us with all its wonderful resources, we are misusing them for our trivial interests. It is the only planet known so far to harbour life, and there is no other place for us to set up base in the near future. It is for our own good that we should learn to take care of this place and to think in a wider spectrum.
This underscores our responsibility to deal with each other with more humanity and to preserve our species and our homeland. It is this planet that we call our ‘Home’, which maybe is a mere ‘pale blue dot’ somewhere in the extragalactic nebula, but it is our only home which is long waiting to be cherished.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Gliese 581g: A Habitable Exoplanet or Just Another Celestial Object Orbiting a Star?“
Recommended Read:
Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space | By Carl Sagan
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Pale Blue Dot: The Iconic Photograph Showing How Microscopic But Brilliant Earth Is appeared first on .
]]>The post Jack Parsons: The Sex Occultist Who Was Key in Sending America to Space appeared first on .
]]>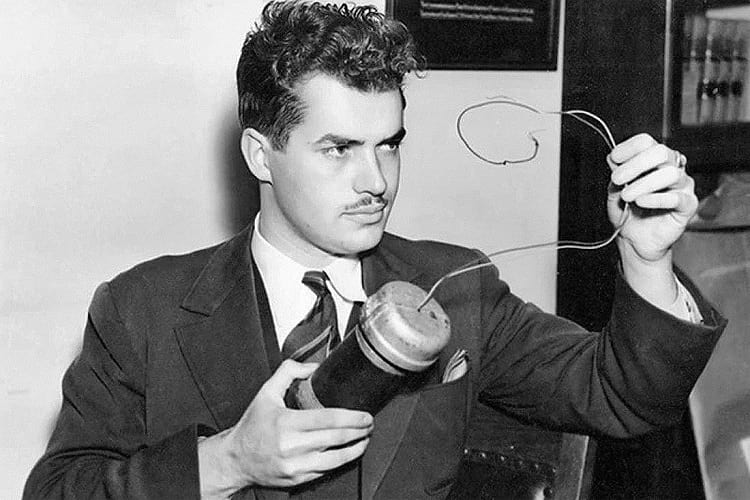
Jack Parsons during a murder trial. (Los Angeles Times / Wikimedia Commons)
Very few people across the world know that the space programme of the United States should actually be credited to a Satanist, Jack Parsons, and not Wernher Von Braun. The later was a German-American aerospace engineer and a pioneer of rocket technology in the US. Wernher Von Braun was also a contemporary of Jack Parsons. Strangely though, most people of the later times never heard of Jack Parsons.
Born on October 2, 1914, as Marvel Whiteside Parsons, Jack’s actual name was John Whiteside “Jack” Parsons. His family was a wealthy family in Pasadena.
Jack lived a colourful, but an eventful life for just 37 years. He died on June 17, 1952, in Pasadena.
Interest in science fiction literature
Thanks to his interest in science fiction literature, Jack is said to have developed an interest in rocketry at a very young age. At the same time at the tender age of 13, Jack is said to have first invoked Satan. Simultaneously, by the age of 14 in 1928, he started to indulge in amateur experiments on rockets with the help of his school buddy Edward Forman.
Jack started his initial experiments in the backyard of his house. There he made gunpowder-based rockets.
Most of his experiments ended up as explosions and he used to have fun. Generally, he used to blow up things with fireworks. As a result, he and Forman were considered as crazy guys at school. The two boys were the kind of kids who were trouble at their school all the time. It was also during this period that the two boys experienced spells and incantations.
The ‘Suicide Squad’
Jack and Forman eventually dropped out of high school. In 1929, when the Great Depression crippled the world, the fortunes of Jack’s family nosedived. He had to drop out of Pasadena Junior College and later from Stanford University due to cash crunch.
In that background, the two friends joined a California-based company known as Hercules Powder Company. The company manufactured armaments. While they were at the Hercules Powder Company, Jack became famous across the nation as a rocket expert.
Later, Jack went to CalTech. In 1934, he teamed up with Forman and approached a graduate student named Frank Malina at the California Institute of Technology. The three formed a
Rocket Research Group that was focused on studying rockets and referred themselves as the ‘Suicide Squad’.
The group was known as the Caltech-affiliated Guggenheim Aeronautical Laboratory (GALCIT) RRG. GALCIT chairman Theodore von Kármán supported the activities of the research group.

Jack Parsons (bottom right) and Edward Forman (top right) along with other GALCIT group members. (NASA / JPL)
Even as World War II was coming to an end, the Rocket Research Group came to be known as the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
Wernher Von Braun credited Jack with US space programme

Wernher Von Braun. (SDASM Archives / Flickr)
Later, of course, Wernher Von Braun acknowledged Jack’s contribution to jet propulsion and rocket technology. In this connection, Wernher Von Braun credited Jack with inventing the American space programme.
It was Jack who actually created the solid fuels that the US later used in the propulsion Polaris nuclear missiles and in the Apollo space missions, said Wernher Von Braun.
During the 1920s and 1930s, rocket science was largely confined to science fiction. In this background, when engineering professor Robert Goddard suggested that a rocket would one day reach the moon, he was mocked at.
Nevertheless, the Suicide Squad’s Jack was a genius at developing rocket fuels. It was a delicate process involving the mixing of chemicals in the right amounts to avoid explosions. During this period he had developed controllable versions of the rocket fuel. NASA later used them.
Aerojet Engineering Corporation (AEC) established
By the 1940s, Malina approached the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) for funds to do research on ‘jet propulsion’. Flush with funds from NAS, the Suicide Squad established a company called Aerojet Engineering Corporation (AEC) in 1943.
The formation of AEC, more or less, legitimized their work. Thus, the Suicide Squad played a vital role in the founding of Jet Propulsion Laboratory at NASA. JPL is the research centre that has been sending ever since spacecraft into the outer space.
With more government involvement, Jack Parsons and his team experienced greater success. More opportunities opened up for Jack. Following this success, the government agencies had to take a closer look into his personal life that had several shocking covert activities.
Jack was engaging in occult activities
While pioneering scientific developments that later put men on the moon, Jack was engaging in occult activities like the Ordo Templi Orientis (OTO). The notorious British occultist Aleister Crowley was leading OTO at that time.
Across Britain and the US, Crowley was said to be “the wickedest man in the world”. It was at OTO that Jack and others took part in strange occult rituals like eating cakes prepared with menstrual blood.
As his career progressed, Jack’s interest in the occult grew manifold. In the early 1940s, Jack was appointed as the West Coast leader of the OTO.
He pumped in money from his rocketry business into his occult activities. He even purchased a mansion in Pasadena to use as a den of hedonism. This gave him an opportunity to explore sexual adventures. During this period, he slept with his wife Helen’s 17-year-old sister Sara in the form of cult-like orgies.
FBI increased its vigil on Jack Parsons’ nocturnal activities
The US government directed the FBI to increase its vigil on Jack Parsons’ nocturnal activities. The FBI found that Jack’s behaviour became a liability to national security. Therefore, in 1943, Jack was forced to quit Aerojet Company and he was paid off his shares. This clearly shows that Jack was expelled from the field that he had actually helped to grow.
With no work on hand, Jack plunged deeper in the occult. During this period, Jack met science-fiction writer L. Ron Hubbard. Hubbard was on the verge of establishing Scientology.
Hubbard urged Jack to summon a goddess to Earth
He urged Jack to summon a goddess to Earth during an outlandish ritual. The ritual itself involved ritual chanting and drawing occult symbols in the air with swords. Then, dripping animal blood on runes and then masturbating to ‘impregnate’ the magical tablets.
During the late 1940s and on the onset of the Red Scare, Jack came under government scrutiny for involving in “sexual perversion” at the OTO. With no hope of getting a government job, Jack started using his expertise on explosives to work on special effects in the movies.
Jack was 37 years old when he died
In spite of this environment, Jack continued to indulge in reckless backyard experiments on rockets. On June 17 in 1952, Jack got a job to work on explosives for a film project. When he was working for his project, an unplanned detonation destroyed his home laboratory and killed him. Jack was 37 years old when he died.

Police investigating the site where Jack Parsons was killed. (Los Angeles Time)
One of the interesting facts includes Jack’s habit of working by day and involving in dark magic during the night.
On Pasadena’s Millionaire’s Row, he purchased a mansion and welcomed his sex-magic cult with open arms. The mansion turned into a den of hedonism.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Space Burial: Making Skies Our Cemetery“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Jack Parsons: The Sex Occultist Who Was Key in Sending America to Space appeared first on .
]]>The post Voyager Golden Records: A Package for the Extraterrestrial from Planet Earth appeared first on .
]]>
Scientist mounting Golden Records on Voyager spacecraft. (JPL / NASA)
It would be a Red Letter Day if alien life is contacted. Motions have been set in place to make this happen but at the very dawn of space exploration it is thought to be hundreds of thousands of years from happening… if at all.

Carl Sagan. (JPL / NASA)
One such motion took place in 1977 when the Voyager Golden Records were launched into the cosmos, two vinyl records which are aboard two spacecraft which launched under the same name. Within the records is a variety of media based on the history of civilization including sounds and images. It is considered a Time Capsule in the sense that it is more likely that humans from the future rather than aliens will find them. Like a message in a bottle, Astronomer Carl Sagan explains it as sending a “…bottle into the cosmic ocean.”
The two spaceships are not destined for anywhere in particular but the most notable of stars – a Goldilocks zone – known as Gliese 445 will be passed in 40,000 years. Needless to say, it is a mission for the future.
Each record is encased in an aluminium casing with a cartridge to play it and a needle. Also, there are instructions on how to use it.
The two sides of the disc

The Sounds of Earth Record Cover. (NASA on The Commons / Flickr)
Illustrations
• The two circles on the top left show states of the Hydrogen atom and the movement of the proton and electron.
• The Square below is to do with rendering. If the record is correctly rendered then this should match the first image.
• An image frame with vertical lines.
• Vertically staggered lines.
• A diagram illustrating how pictures are made. Showing video signals and binary codes.
• Binary arithmetic explaining how the record should be played.
• Overall play time of record.
• Pulsar map showing the location of our Sun and the frequency of some pulsars.
The information is very technical, related to the actual playing of the record which holds the majority of the content.
There is also a clock – in a sense – electroplated onto the cover of the record. An extremely clever clock built to last billions of years. It is the element Uranium-238 which has a radioactivity of 0.00026 microcuries to be precise. The Uranium will decay to half of its original radioactivity value in 4.5 billion years meaning this can show the time since launch. Because scientifically speaking, Uranium-238 has a half-life of 4.468 billion years.
However, the pulsar map should also be able to show this.
Within the record are images selected by a NASA committee. The aforementioned Carl Sagan chose 115 images in Analog form.
There are some beautiful and bizarre photos on the vinyl. All 116 are in this link.
Also, there are many sounds, music and greetings from fifty-five languages including 5 archaic languages. There is Akkadian, a dead language spoken in the Middle East about six thousand years ago and Wu, a modern Chinese dialect. Here is a translation to English of every greeting:
- Akkadian– “May all be very well”
- Amoy (Min dialect)– “Friends of space, how are you all? Have you eaten yet? Come visit us if you have time.”
- Arabic – “Greetings to our friends in the stars. We wish that we will meet you someday.”
- Aramaic– “Peace”
- Armenian – “To all those who exist in the universe, greetings.”
- Bengali – “Hello! Let there be peace everywhere.”
- Burmese – “Are you well.”
- Cantonese – “Hi. How are you? Wish you peace, health and happiness.”
- Czech – “Dear Friends, we wish you the best.”
- Dutch – “Heartfelt greetings to everyone.”
- English – “Hello from the children of planet Earth.”
- French – “Hello everybody.”
- German – “Heartfelt greetings to all.”
- Greek – “Greetings to you, whoever you are. We come in friendship to those who are friends.”
- Gujarati – “Greetings from a human being of the Earth. Please contact.”
- Hebrew – “Peace.”
- Hindi – “Greetings from the inhabitants of this world.”
- Hittite– “Hail.”
- Hungarian (Magyar) – “We are sending greetings in the Hungarian language to all peace-loving beings in the Universe.”
- Ila (Zambia)
“We wish all of you well.” - Indonesian
“Good night ladies and gentlemen. Goodbye(,) and see you next time.” - Italian – “Many greetings and wishes.”
- Japanese– “Hello? How are you?”
- Kannada (Kanarese)
“Greetings. On behalf of Kannada-speaking people, ‘good wishes.'” - Kechua (Quechua) – “Hello to everybody from this Earth, in Kechua language.”
- Korean– “How are you?”
- Latin– “Greetings to you, whoever you are; we have good will towards you and bring peace across space.”
- Luganda (Ganda) – “Greetings to all peoples of the universe. God give you peace always.”
- Mandarin Chinese– “Hope everyone’s well. We are thinking about you all. Please come here to visit when you have time.”
- Marathi– “Greetings. The people of the Earth send their good wishes.”
- Nepali– “Wishing you a peaceful future from the earthlings.”
- Nguni (Zulu)– “We greet you, great ones. We wish you longevity”
- Nyanja– “How are all you people of other planets?”
- Oriya– “Greetings to the inhabitants of the universe from the third planet Earth of the star Sun.”
- Persian– “Hello to the residents of far skies.”
- Polish– “Welcome, creatures from beyond the outer world.”
- Portuguese– “Peace and happiness to all.”
- Punjabi– “Welcome home. It is a pleasure to receive you.”
- Rajasthani– “Hello to everyone. We are happy here and you be happy there.”
- Romanian – “Greetings to everybody.”
- Russian – “Greetings! I Welcome You!”
- Serbian – “We wish you everything good from our planet.”
- Sinhalese – “Wish You a Long Life.”
- Sotho (Sesotho)– “We greet you, O great ones.”
- Spanish– “Hello and greetings to all.”
- Sumerian – “May all be well.”
- Swedish – “Greetings from a computer programmer in the little university town of Ithaca on the planet Earth”
- Telugu – “Greetings. Best wishes from Telugu-speaking people.”
- Thai – “We in this world send you our goodwill”
- Turkish – “Dear Turkish-speaking friends, may the honors of the morning be upon your heads.”
- Ukrainian – “We are sending greetings from our world, wishing you happiness, goodness, good health and many years.”
- Urdu– “Peace on you. We the inhabitants of this earth send our greetings to you.”
- Vietnamese – “Sincerely send you our friendly greetings.”
- Welsh– “Good health to you now and forever.”
- Wu – “Best wishes to you all.”
There are 90 minutes of music, Eastern and Western classics, as well as traditional songs from all corners of the world, are included. Here is a list of all of the music on the record:
- Bach, Brandenburg Concerto No. 2 in F. First Movement, Munich Bach Orchestra, Karl Richter, conductor. 4:40
- Java, court gamelan, “Kinds of Flowers,” recorded by Robert Brown. 4:43
- Senegal, percussion, recorded by Charles Duvelle. 2:08
- Zaire, Pygmy girls’ initiation song, recorded by Colin Turnbull. 0:56
- Australia, Aborigine songs, “Morning Star” and “Devil Bird,” recorded by Sandra LeBrun Holmes. 1:26
- Mexico, “El Cascabel,” performed by Lorenzo Barcelata and the Mariachi México. 3:14
- “Johnny B. Goode,” written and performed by Chuck Berry. 2:38
- New Guinea, men’s house song, recorded by Robert MacLennan. 1:20
- Japan, shakuhachi, “Tsuru No Sugomori” (“Crane’s Nest,”) performed by Goro Yamaguchi. 4:51
- Bach, “Gavotte en rondeaux” from the Partita No. 3 in E major for Violin, performed by Arthur Grumiaux. 2:55
- Mozart, The Magic Flute, Queen of the Night aria, no. 14. Edda Moser, soprano. Bavarian State Opera, Munich, Wolfgang Sawallisch, conductor. 2:55
- Georgian S.S.R., chorus, “Tchakrulo,” collected by Radio Moscow. 2:18
- Peru, panpipes and drum, collected by Casa de la Cultura, Lima. 0:52
- “Melancholy Blues,” performed by Louis Armstrong and his Hot Seven. 3:05
- Azerbaijan S.S.R., bagpipes, recorded by Radio Moscow. 2:30
- Stravinsky, Rite of Spring, Sacrificial Dance, Columbia Symphony Orchestra, Igor Stravinsky, conductor. 4:35
- Bach, The Well-Tempered Clavier, Book 2, Prelude and Fugue in C, No.1. Glenn Gould, piano. 4:48
- Beethoven, Fifth Symphony, First Movement, the Philharmonia Orchestra, Otto Klemperer, conductor. 7:20
- Bulgaria, “Izlel je Delyo Hagdutin,” sung by Valya Balkanska. 4:59
- Navajo Indians, Night Chant, recorded by Willard Rhodes. 0:57
- Holborne, Paueans, Galliards, Almains and Other Short Aeirs, “The Fairie Round,” performed by David Munrow and the Early Music Consort of London. 1:17
- (The) Solomon Islands, panpipes, collected by the Solomon Islands Broadcasting Service. 1:12
- Peru, wedding song, recorded by John Cohen. 0:38
- China, Ch’in, “Flowing Streams,” performed by Kuan P’ing-hu. 7:37
- India, raga, “Jaat Kahan Ho,” sung by Surshri Kesar Bai Kerkar. 3:30
- “Dark Was the Night,” written and performed by Blind Willie Johnson. 3:15
- Beethoven, String Quartet No. 13 in B flat, Opus 130, Cavatina, performed by Budapest String Quartet. 6:37
A message from the US President at the time Jimmy Carter and UN Secretary are also included. The former President reads:
“This Voyager spacecraft was constructed by the United States of America. We are a community of 240 million human beings among the more than 4 billion who inhabit the planet Earth. We human beings are still divided into nation states, but these states are rapidly becoming a single global civilization.
We cast this message into the cosmos. It is likely to survive a billion years into our future, when our civilization is profoundly altered and the surface of the Earth may be vastly changed. Of the 200 billion stars in the Milky Way galaxy, some–perhaps many–may have inhabited planets and spacefaring civilizations. If one such civilization intercepts Voyager and can understand these recorded contents, here is our message:
This is a present from a small distant world, a token of our sounds, our science, our images, our music, our thoughts, and our feelings. We are attempting to survive our time so we may live into yours. We hope someday, having solved the problems we face, to join a community of galactic civilizations. This record represents our hope and our determination, and our good will in a vast and awesome universe.”
Already by 1990 the Voyagers had gone further than Pluto and ultimately outside our solar system. The mission is extremely romantic and symbolic in the sense that it is extremely hopeful that aliens will be able to decipher it. Even for them to even have the correct anatomy and perceptions to operate the device. At this stage it is perhaps better to view the Golden Records as a Time Capsule rather than an attempt of contacting (the) other life. The director of the project Carl Sagan admits that also. But who knows how the future will pan out.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “The Mysterious Wow! Signal: Aliens? A Comet? Or Just a Glitch?“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Voyager Golden Records: A Package for the Extraterrestrial from Planet Earth appeared first on .
]]>The post A Glimpse into the Exciting World of Space Tourism appeared first on .
]]>
Artistic impression of Aurora Space Station interior, a concept design of the world’s first luxury space hotel by Orion Span. (© Orion Span)
More than 100 years ago, Russian scientist Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky helped the erstwhile USSR’s space programme. Thus, deaf Tsiolkovsky is a pioneer in rocket science.
After years of rejection, Tsiolkovsky became an inspiration to later Soviet scientists in the areas of space travel and space colonization.
During the 19th and early 20th centuries, the idea of space travel was unthinkable except in scientific papers. To make space travel possible, the Soviets developed a spacecraft that flew around the Earth in outer space sometime in 1957. The first living creature to orbit the Earth was Laika, a 2-year-old terrier mutt. The terrier mutt flew into Earth’s orbit and paved the way for modern space exploration.
Commercial activities
In 1961, a 27-year-old Soviet cosmonaut named Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin became the first human to travel in space aboard spacecraft Vostok 1. Since then humans set their foot on the Moon, sent spacecraft to planets like Jupiter, Saturn, and Pluto and even landed a rover on Mars.
Till recently, all orbital spacecraft with human passengers have been developed as governmental ventures. But in the past few years, private participation has seen significant growth. Corporate entities like Virgin Galactic, SpaceX and Blue Origin have taken quick strides in spacecraft development for commercial activities.
With the result, taking a trip to outer space is no longer the matter of science fiction for humans. However, space travel or space tourism continues to be an expensive affair. But, soon it could become a viable scientific and holiday destination thanks to organizations promoted by Richard Branson, Elon Musk and Jeff Bezos.
These and other companies are today offering to take space tourists for astronomical fares. And, there is no need for such tourists to be savvy with scientific knowledge. They, however, need to undergo fitness tests under and get trained under the guidance of NASA officials before the lift-off.
What is space tourism?
The term refers to travelling into space by humans for leisure or recreational purposes. As of now, there are three types of space tourism, i.e. lunar space tourism, orbital and suborbital tourism.
Lunar space tourism
Elon Musk’s aerospace company SpaceX is planning to send two space tourists around the Moon in its reusable Big Falcon Rocket (Starship). The space travel, known as a Moon Loop, is expected to take place sometime in 2023.
While identifying the passenger on this trip, Elon Musk said Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa is the lucky tourist on the Moon mission. It may be recalled that the last human Moon mission was in 1972 – the Apollo mission.
Orbital space tourism
Till today, the Russian Space Agency is the only organisation to offer orbital space tourism. In all, seven private persons paid their way to take part in orbital space tourism to date. This kind of tourism became possible in 2001 when the Russian company called MirCorp entered into a pact with a US firm named Space Adventures Ltd.
In April 2001, American businessman Dennis Tito flew into space to become the world’s first orbital space tourist. He paid $20 million to the Space Adventures for the flight and a 7-day stay on the International Space Station (ISS).

Dennis Tito (left), Talgat Musabayev (middle), and Yuri Baturin (right), the crew of Soyuz TM-32. (NASA)
Speaking after Dennis’ space journey, President of Space Adventures Tom Shelley said six others spent time on ISS. They included South African computer millionaire Mark Shuttleworth, American businessman Gregory Olsen, and Iranian-born American entrepreneur Anousheh Ansari.
The remaining orbital space tourists were American billionaire Charles Simonyi and American video game developer Richard Garriott. This tourism programme was, however, cancelled in 2010.
Suborbital space tourism
Spacecraft under this category fly up to an altitude of 100–160 km. At that height, passengers experience weightlessness for 3 to 6 minutes and they can get a view of the star field and that of the Earth’s curve.
Till the beginning of 2019, not one suborbital space tourism flight took off in spite of being affordable. The flight cost is projected in the range of $200,000 per passenger. Meanwhile, Virgin Galactic’s spacecraft known as ‘SpaceShipTwo’ is likely to achieve supersonic speed and take its first passengers on suborbital space tourism.
‘SpaceShipTwo’ is expected to be launched from an altitude of 50,000 feet. It is, then, likely to get a forward thrust from a jet aircraft known as WhiteKnightTwo. SpaceShipTwo is scheduled to carry six tourists and to two pilots on the trip. When? Branson is yet to decide the date. It is, however, confirmed is that Branson will be aboard the flight.

SpaceShipTwo. (Virgin Galactic / Mark Greenberg)
Zero gravity
In May 2018, Virgin Galactic’s SpaceShipTwo achieved supersonic speed in its second test run. When humans travel at such speeds, a lot of pressure will be exerted on their bodies. Interestingly though, when humans enter the zero gravity zone there is absolutely no pressure on their bodies making them weightless.
Also in the zero-gravity zones, there is a danger for humans to lose their bone density. Their bones could become brittle and there are chances of their bones breaking when they return to Earth.
Health risks
Similarly, human muscles and heart don’t work as required in zero gravity conditions. They, therefore, turn weak. To counter these and other health issues, NASA prepares the tourist recruits with hard workouts before, during, and after the space journey.
In spite of NASA’s training, experts believe that space tourists should be prepared to accumulate a high dose of radiation during the trip.
In addition to health risks, the tourists should be prepared for an inevitable accident in outer space. If the inevitable happens it will be extremely traumatic to the kith and kin of the tourists. Therefore, space tourism should be bracketed as a dangerous sport.
Space settlement
Al Globus writes in his article titled ‘Space Tourism Leads to Space Settlement’, space tourism could ensure low-cost and safe transportation for space settlements in future. Stating that space tourism could spur the market for cheaper space transport, Al Globus writes space tourism market will become larger than expected.
Futurists are already predicting settlements on Moon, Mars or asteroids. They hope that humans could have larger living spaces, improved resources and energy.
Futurists like Patrick Colins predicted that millions of tourists could fly into space very soon if the travel cost drops to $10,000 per person. Within 25 years from today, they feel orbital tourism will be much cheaper.
Reusable space vehicles
For this to happen, private companies need to manufacture passenger launch vehicles at drop-down prices.
According to Vice-president at Spaceport America Bill Gutman, reusable space vehicles are the key to the future of space tourism. Such vehicles will surely cut down overall manufacturing costs and slash travelling costs.
Cost of space tourism
With space vehicle manufacturing and travelling costs down, the focus of newer entrants will be on positioning space hotels in Earth’s orbit. Russia’s Orbital Technologies has already prepared a blueprint for building a space hotel that can accommodate seven guests. They are also preparing a blueprint for Lunar Colonies with a focus on leisure.
If California-based start-up Orion Span’s plans come true then the company is proposing to position its luxury space hotel in Earth’s orbit by 2021. The affordable orbital leisure destination named “Aurora Station” could begin to accommodate guests by 2022.
Orion Span’s Frank Bunger reveals that it could cost a guest at least $9.5 million for a 12-day stay on Aurora Station. Bunger disclosed that the space hotel, which is being built in the Bay Area, can accommodate two crew members and four guests. Bunger says that if demand grows, additional modules called space condos can be attached to the space hotel.
But with costs still astronomical, what could be the future of space tourism? It could be similar to the history of the airline industry. Initially, only wealthy people, politicians and government officials could afford to fly. With ticket costs crashing and potential passengers growing, the airline industry’s business prospects soared.
Therefore, recognising the imminent potential in space tourism, the government and private sectors should solve the problem of astronomical manufacturing costs and boost space travel.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Space Advertising: The Race to Advertise in Outer Space“.
Reserve Now:
Orion Span
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post A Glimpse into the Exciting World of Space Tourism appeared first on .
]]>The post Space Advertising: The Race to Advertise in Outer Space appeared first on .
]]>
NASA astronaut Dale A. Gardner jokingly holding a “For Sale” sign for the satellites behind him. (NASA)
Outer space begins from just over 80 km above the earth’s surface. For advertisers, it is the final frontier for capturing and holding consumer attention. People around the world have grown accustomed to and jaded about seeing or hearing advertisements in all the usual places – television, radio, movies, roadside banners, billboards, magazines, books, and so on. They may even ignore these advertisements with repeated viewing.
Advertisers hope that it won’t be the same case if they start advertising in outer space. Although, if you really think about it and consider human nature, there is no reason why the outcome should be any different. It is true that an advertisement spread out in outer space will have a wider reach. It may be seen by billions of potential consumers, no matter where they are located on the planet, no matter if they have digital or electronic devices or not.
Advertising attempts in outer space
There were plans to put up lights on a formation of satellites in the low earth orbit to mimic a billboard, but these were shelved for various reasons. The illumination from the advertisements would have shone as brightly as the moon, obstructing astronomical observations. There would have been an on-going risk of collision with other satellites, spacecraft and also the risk of being hit by meteorites. Such collisions could lead to the adding problem of space debris.
There were objections from the public as the advertisements would have been too obtrusive to avoid, being always visible high above to the naked eye. Such advertisements would also be very expensive to create and launch and technologically difficult to change often.
In 1993, the United States-based company Space Marketing Inc. attempted a space billboard project that flopped. Since then, no other company has attempted what many people consider to be a ludicrous idea. Even so, the US government has banned all billboard advertisements in outer space that can be seen without the aid of telescopes and other devices. There are also several international organizations that are campaigning to put limits on obtrusive space advertising.
Some outlandish outer space advertising
The French Ring of Light project, meant to celebrate the 100th anniversary of the Eiffel Tower, would have competed with the moon for sheer brightness. The project was to have an inflatable ring with a circumference of 24 km and this ring would have had reflective Mylar balloons attached to it at various points. If the project had been carried out, the organizers would have launched the ring to a height of over 800 km. Fortunately, the project was abandoned and will not be ruining our view of the moon.
Meanwhile, Coca-Cola and Google proposed to use the moon itself as a billboard. They planned to use high-powered lasers to beam their logo onto to the moon’s surface. Technological and legal challenges ended those plans.
Then there was the Znamya project that many people considered to be an advertisement for the Russian space agency. The project launched satellites to direct sunlight to the Arctic area and these satellites also to lit up some areas of Europe. The Znamaya 2.5 project, which could have lighted up areas in the US, was abandoned after it failed to launch.
Outer space advertising successes
Advertising by product placement and publicity stunts have seen some success in the outer space advertising arena.
In 2000, Pizza Hut bought advertising space on the unmanned Proton rocket that Russia launched to carry the Zvezda module to the International Space Station. The new 30-foot Pizza Hut logo was painted on the side of the rocket and got the company noticed by a lot of people around the world. The next year, Pizza Hut delivered a 6-inch salami pizza in a vacuum-sealed container to the International Space Station. The first pizza to be eaten in space had to undergo several rounds of testing to meet space food standards. The free press coverage of the event and the details of all the planning and preparation for it was worth millions of advertising dollars to Pizza Hut. Plans to develop an outer space food delivery service are, however, nowhere in sight.
Other famous publicity stunts involved Kodak having their logo and a slogan painted on the durability testing material on the outside of the International Space Station and Pepsi having a cosmonaut float a replica of their soda can outside the Russian Mir space station. The cost of these stunts varied from half a million dollars to over five million dollars.
The Japanese reporter, Toyohiro Akiyama, was the first journalist to go on a spaceflight in 1990. The Tokyo Broadcasting System (TBS) paid around $10 million to the Russian space agency to send him on the Soyuz TM-11 expedition to the Mir Space Station. TBS also had their logo painted on the Soyuz rocket. Aware that TBS would receive enormous publicity from this, other companies like Sony, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, and Unicharm also availed of the opportunity to place their logos on the launch shroud of the rocket.

Elon Musk’s Tesla Roadster in space. (SpaceX)
In February 2018, Elon Musk’s Tesla Roadster was selected as a dummy payload on the Falcon Heavy rocket when SpaceX launched it for a test flight. The rocket put the car into a heliocentric orbit. The onboard camera provided a livestream of the event for over four hours and millions of people viewed it. It turned out to be a great marketing stunt for Tesla’s cars as well as publicity for SpaceX’s space exploration ventures.
Advertising related to outer space
The 1960s and 1970s saw brands like Pillsbury and Tang promoting their products as being used by astronauts in outer space.
In 2015, the South Korean carmaker, Hyundai, released an online video showing 11 Genesis cars making an image with their tire tracks on the Delamar dry lake bed in the Nevada desert. The image spanning 5.5 square kilometres was filmed by the company to be a message from a daughter to her father who saw it from the International Space Station. The millions of views that this emotional story got increased Hyundai’s brand value.
The Axe brand of Unilever SA, assisted by the astronaut Buzz Aldrin, held a contest in 2013 to give people a chance to book seats on commercial space flights organised by the Netherlands-based Space Expedition Corp.
Legality of advertising in outer space
The 1967 Outer Space Treaty states that activities planned in outer space, which includes the moon and other bodies in space, should not cause any harm or interfere in the peaceful exploration of outer space. There are no specific laws regarding using satellites or the moon or anything else in outer space for advertising purposes. Other than the US ban on obtrusive billboards, there are no national laws regulating advertising in the space industry. The advertising business has laws relating to how true the claims made by advertisers about their products are, but there are no laws about how true the stories used to sell the products can be. It may be possible for companies to use laws about unfair competitive advantage to prevent other companies from using outer space as an advertising medium.
Future of outer space advertising
Individuals and institutions, who participate in competitions for developing space vehicles such as Google Lunar X PRIZE, plan on getting the necessary funding from sponsorship deals with large international brands. Private space exploration companies, as well as national space programs with increasingly limited budgets, are also looking at ways to raise funds. The success of some of these publicity stunts may encourage them to get funding from consumer product companies willing to pay for delivering their own branded products into outer space.
Other companies can pay to have their logos placed on equipment used on spacecraft and satellites. Companies can also launch their own branded payloads into the International Space Station, film the launch and distribute the video online to get publicity for their experiments and research. This type of advertising is still very expensive, however, and is not likely to become ubiquitous anytime soon.
Advertisers are always on the lookout for unique and entertaining ways to market products and services, and no one can predict what forms of advertising could become possible in outer space.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Space Burial: Making Skies Our Cemetery“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Space Advertising: The Race to Advertise in Outer Space appeared first on .
]]>The post Znamya Satellite: Russia’s Space Mirror Deflects Sunlight to Light up Arctic Region for Brief Period appeared first on .
]]>
Znamya satellite. (QSI / MIR)
The Russian scientists planned to capture the sunlight on the space mirrors and deflect the same onto Earth during the night. The idea was to increase daylight hours in the Arctic regions of Russia and northern Europe. Also, the idea was to provide solar energy to people in these regions.
Znamya is the Russian word for a banner. It was a Russian satellite. The Space Regatta Consortium (SRC) had developed Znamya series under the Russian Space Mirror Project. A corporation named Energia was behind the SRC project.
The experiment with Znamya was not successful. That is why, SRC successfully deployed Znamya-2 on the night of February 4, in 1993. It carried a payload of space mirrors that had a 20m diameter. They were circular in form and had 5mm thickness. The space mirrors were made of aluminized PETF (Mylar) film that had an areal density of 22 g/2cm.
The mirrors were split into eight sections with gaps between them. The mirrors had an unfolding mechanism inside Progress M-15, a cargo space vehicle. Before deploying the space mirrors, Progress M-15 disengaged from MIR space station.
Znamya Satellite: Idea was to increase daylight hours
Znamya-2’s deployment of space mirrors was a success. True to its purpose, the space mirrors succeeded in deflecting the sunlight and lighted up the night sky for a brief moment. The redirected beam appeared brighter than the moon. The brightened area was 5 to 6 km wide.
Interestingly, the redirected beam passed across regions like the Atlantic Ocean, Europe, and Russia. How did the deflected sunlight appear to people on Earth? For some, it appeared like a bright star. For astronauts orbiting the Earth, it appeared like a pale light.
The experiment lasted a few days
The success of the Znamya-2 experiment can be looked from the feasibility of illuminating the earth during night time. However, the experiment lasted for a few days as the giant mirrors deorbited and went up in flames while re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere.
Following the partial success of Znamya-2 experiment, SRC conceived and developed Znamya-2.5. The idea was to deploy reflectors of 25m diameter. The design and materials used in Znamya-2.5 were similar to Znamya-2.
Znamya-2.5 had three chief goals
Znamya-2.5 had three chief goals: a) to validate improvements made in the film structure, b) to test the new light (Novy Svet) illumination capability, and c) to examine the stability of the film structure and the system.
SRC deployed Znamya-2.5 on February 4 of 1999. But, sadly, there was an error in the software and the mission operations due to which the whole reflector apparatus plunged into the ocean.
Ever since then neither Russia nor any other country experimented with solar mirrors. Had the Znamya experiment succeeded in all respects, the Russians planned to send dozens of space mirrors into Earth’s orbit.
Origins
The foundation for the Znamya experiment was laid in the 1980s, especially during the Cold War period. The Soviet Union military conceived of a new technology to wage space war against its enemies. At the same time, the Soviets desired to boost productivity in the cities and in farmland.
Znamya’s lead engineer was the maverick Vladimir Syromyatnikov, who was behind the spacecraft that propelled Yuri Gagarin into space in 1961. Syromyatnikov had a brilliant space engineering mind.
It was Syromyatnikov’s passion for solar sails that led to the Znamya experiment. But, after the Znamya experiment’s partial failure Syromyatnikov returned to the drawing board to improve the docking mechanisms for Znamya 3. But with no fresh funding forthcoming, his plans remained on the drawing board.
The costs involved in the Znamya experiment were sky high. The hardware costs alone of Znamya 2 were in the region of $10 million. For the Znamya 3 experiment, Syromyatnikov wanted funds in the region of $100 million. He believed that the Znamya experiment would turn profitable in three years only.
While Russia’s Znamya experiment was on, there were worldwide protests from diverse communities like environmentalists, scientists, astronomers and humanitarian groups.
Controversies
Astronomers slammed the experiment saying it would hinder space observation from Earth. Environmentalists said the absence of nighttime could cause physiological disorders like sleep deprivation among humans and animals.
Syromyatnikov’s Znamya experiment was a path-breaking one. Today, it’s near impossible for us to visualise the vision behind the experiment. The vision was to have multiple space mirrors in Earth’s orbit to regulate nightlife in a sleepless world.
Sadly, Vladimir Syromyatnikov, one of the greatest astronautical engineers in the world passed away in September 2006.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Lost Cosmonauts of USSR: Did the Soviet Union Cover up its Secret Cosmonaut Casualties?“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Znamya Satellite: Russia’s Space Mirror Deflects Sunlight to Light up Arctic Region for Brief Period appeared first on .
]]>The post Kármán Line: The Hypothetical Line That Delineates the Earth’s Atmosphere from Outer Space appeared first on .
]]>
Photo of earth from International Space Station. (NASA / ISS043-E-86375)
The Kármán line is a hypothetical boundary located 100 km above sea level, designating the end of the earth’s atmosphere and the beginning of outer space. It is named after the Hungarian scientist Theodore von Kármán. He suggested its creation for the clear-cut separation of the fields of aeronautics and astronautics.

Theodore von Karman. (Theodore von Karman / Flickr)
Understanding the Earth’s atmosphere
The earth’s atmosphere is what we commonly call air, a dense mixture of gases whose physical properties affect everything moving within it. As you move up from the earth’s surface, the density of the air progressively decreases to eventually meld into the vacuum of outer space. There is no definite boundary where this happens. Experts estimate the distance to be between 100,000 km and 190,000 km above the earth’s surface. This area is the last layer of the atmosphere and is called the exosphere. The layer below this is called the thermosphere, which is between 500 km and 1,000 km above the earth’s surface. The mesosphere extends from a height of 50 km to 85 km; the air here is too thin to breathe. The stratosphere extends from 10 km to 50 km above the ground. The lowest layer with a height of about 10 km is called the troposphere. We live in this layer and the formation of clouds occurs here. Scientists defined the boundaries of these spheres at the points where there are discernible changes in the temperature of the air.
Satellites in the Earth’s atmosphere
Satellites orbit the earth at distances ranging from 160 km to 36,000 km above the earth’s surface. The International Space Station orbits at around 400 km. The Hubble Space Telescope orbits at 569 km. All these distances are within the earth’s atmosphere, but we talk about them orbiting in space as the atmospheric conditions at those distances have a negligible effect on their operation. So, the vehicles used to travel to the International Space Station and to repair satellites are called spacecraft and the people travelling in these vehicles are called astronauts.

Hubble Space Telescope. (NASA Hubble Space Telescope / Flickr)
Airplanes flying in the Earth’s atmosphere
An aircraft moves relative to the air and that movement is what enables its wings to generate the lift necessary to keep it flying forward. Passenger jets usually fly in the lower part of the stratosphere as the airflows there are less turbulent than in the troposphere. If they fly higher up into the mesosphere, they have to increase their speed to generate the necessary wing lift in the thinning air. Above the mesosphere, there is not enough air to provide any lift to an aircraft’s wings and it is pulled downwards by gravity. To stay aloft, the aircraft would have to increase its speed to touch orbital speed and then would have to follow the earth’s curvature.
The Kármán line
So, the highest distance above the earth’s surface where there is enough air for an aircraft to get the wing lift to fly in a straight line is considered by some people to be the end of the atmosphere.
Theodore von Kármán calculated this distance to be around 83 km and suggested that the value be rounded up to 100 km to make it easier to remember. The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI), the governing body for air sports, maintains separate records for air sports and space flights. It uses the Kármán line to differentiate between the two. However, not all countries and organizations are in unanimous agreement on the location of the Kármán line. Some countries consider the distance to be 50 km above the earth’s surface and other countries consider the distance to be 80 km.
The importance of the Kármán Line
Just as a country’s territorial rights extends for about 22 km in the surrounding seas and oceans, beyond which distance oceans are considered international waters, a country’s territorial rights also extend upward into the atmosphere. Hence, it is necessary to have something like the Kármán line to delineate airspace governed by each country from outer space over which no country can claim sovereignty. All countries have rules and regulations for passenger aircraft flying in their airspace.
Private space exploration companies, who are developing passenger spacecrafts, would have to know the distance above which they can fly to avoid this jurisdictional area. Another issue is whether these passengers can call themselves astronauts. There are countries that are opposed to defining a boundary for military reasons, and there are some countries that want a definite boundary for the same reason. Fighter aircrafts and missiles, which can travel higher than passenger aircrafts, could fly through sovereign airspaces, provoking military aggression.
There are satellites in low elliptical orbits whose distance from earth varies, based on their position. The closest distance is called perigee, and, for some satellites, this distance is below 100 km. Are the satellites sometimes orbiting in space and sometimes in the atmosphere?
National space institutions as well as private research institutions launch satellites for various purposes. What are the laws that should be applied if there are any disputes over the use of satellites while passing through national airspace?
There are some international rules and regulations for operating in what is considered outer space, and, so far, there have been no problems because of the lack of a definite boundary where this outer space begins. But that does not preclude issues from arising in the future as there is an increase in space exploration and space utilization activities.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “The Wallace Line: The Invisible Line of Bio-Diversity in the Indian Ocean“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Kármán Line: The Hypothetical Line That Delineates the Earth’s Atmosphere from Outer Space appeared first on .
]]>The post Space Food: What Do Astronauts Eat Outside the Earth’s Atmosphere? appeared first on .
]]>
Space food presentation at Space Food Systems Laboratory in Johnson Space Center. (NASA)
Going out in space is one tough task that astronauts have to face. They are given rigorous training for months before their journey. They are meticulously prepared for a mission, man once only dreamt of. Although it may seem easy to us, but the moment a space explorer steps into the area of zero gravity, nothing is easy anymore.
Zero gravity not only hampers an astronaut’s psychological state but also disturbs their regular physiological functions. And to maintain a strict balance between both, it is necessary that the ones going in space make sure they eat the right kind of food. But did you know that those who travel in space pack special kind of foods with them, lest it becomes a major cause of concern for them and their space shuttle?
The need for space food
Long before freeze-dried and processed foods packed in small tubes were carried on space flights, scientists did not know that a procedure as simple as eating would cause trouble to astronauts. It was only when Russian cosmonaut Gherman Stepanovich Titov experienced space sickness for the first time and vomited his entire stomach’s contents, did researchers realize that food was one of the major factors that needed careful planning before men and women were sent out. A celebrated figure across the globe today, Titov travelled in space on August 6, 1961 following in the footsteps of his fellow countryman Yuri Gagarin. It was this ‘rare event’ that he experienced on Vostok II that brought on the need for special space food for astronauts.
A regular helping of routine food, which resulted in upset tummies, was completely done away with to avoid astronauts falling sick in space in the future. Bite-sized, dehydrated foods that were not just nutritious but also tasty, light-weight, able to be refrigerated and eaten as and when required, specially packaged space foods became the norm. This heralded a new era of supplying meals to astronauts that neither meddled with human physiology in space nor did it affect the astronaut’s psychological condition, deviating him/her from the task at hand.
First food in space
Learning from previous experience, John Glenn, an American astronaut, onboard Friendship 7 in 1962, was issued foods in compact tubes, from which he could easily eat while in a state of zero gravity. He became the first American to eat food in space on board a space shuttle. A combination of applesauce with sugar tablets in water was considered the first space food that Glenn carried with him.
Scientists found out that astronauts could easily ingest, swallow and even digest food while experiencing total weightlessness and so special meals that did not hamper with the natural process of eating began to be issued to astronauts from then on. Some packaged meals issued to Glenn also contained pureed meat and vegetables, which he could directly ingest from a tube, without spilling it around or letting it float away in a gravity-less environment.
Preparing food for space
Before packed meals are sent on board a space vehicle, it is carefully prepared by specially trained chefs, who know what it takes to transport food out of the Earth’s orbit. There are a variety of procedures that are undertaken before packaging and sending food in space. It is either freeze-dried, irradiated or thermo-stabilized, along with a host of other processes that make meals edible in space.
In the freeze-drying procedure, the food is first cooked and then quickly frozen in very low temperatures before putting it inside a vacuum chamber, where the water from it is dried off. This process does not compromise on the taste or the quality of the food. Some foods are also preserved before they are freeze-dried. Irradiated foods are packed in foil pouches before being exposed to gamma radiation to kill off the bacteria dwelling inside them. Irradiated foods do not pose a threat to human life. Thermo-stabilizing foods mean completely destroying the germs and microorganisms from certain food items so that they can be stored for a longer period of time before eating. Fish and most fruits undergo thermo-stabilization before being packed for space delivery.
Nuts and cookies are carried as they are, only that they are coated with gelatin so they don’t end up in crumbs that could float inside the pod. Some dried fruits like apricots, peaches, plums and pears are stripped of some of their moisture and issued to astronauts to be carried outside the Earth’s atmosphere.
Long before gourmet meals, just the way we eat on Earth were sent out in space for astronauts’ consumption, less appetizing and almost flavorless meals were issued to them. Packed in tubes, which had to be squeezed out like toothpaste, along with powdered granules of fruit juices or beverages were supplied to them. Astronauts then had to directly add hot water to the powder to rehydrate them before they could enjoy a hot cup of coffee or add cold water to have a sip of their favourite orange juice.

Russian space food. (Wikimedia Commons)

Ramen with an inlet to add hot water before consumption. (Tnk3a / Wikimedia Commons)
Before sophisticated methods like refrigerating and thermo-stabilizing were introduced onboard a spaceship, which are hassle-free methods of food preparation, freeze-drying was one of the most trusted ways of preparing food in space. Astronauts made use of hot or cold water guns, which injected water directly into the zip-locked pouches of food or plastic packets to rehydrate them so as to be eaten. Some space suits also had in-suit drinking devices, which were to be used in case of emergencies. These in-suit devices provided liquid foods in special ports, which were fitted in their helmets so that when things went wrong in their shuttle, they could live in space for a while with food stored in their suits.
Introduction of luxury space food
After John Glenn had the good fortune of eating pureed meat and vegetables, space food saw many alterations to suit the human physiology. More and more sophisticated, comfort foods were introduced, which were not only palatable but healthy as well. Squeeze tubes were discarded and thermo-stabilized pouches or wetpacks came into the picture. These packs made out of flexible aluminium foil or sterilized plastic kept food moist for a longer period of time and didn’t need rehydrating before consumption. These wetpacks allowed astronauts to enjoy bites of turkey, bacon and shrimp, helpings of chicken soup, tuna salad and even have cornflakes or beef sandwiches for breakfast, along with chocolate and butterscotch pudding for dessert.

Food trays provided in space shuttle have straps to help secure them on walls or platforms before using them. (RadioFan / Wikimedia Commons)
The Apollo crew was the first to be provided with utensils, including a spoon bowl, which was a plastic container with dehydrated food already packed inside. Hot water needed to be injected into the bowl to rehydrate the meal, which the astronauts could eat with a spoon. The wetness of the food allowed it (to) stick easily to the spoon and not float away in the shuttle. Luxury foods like chocolate brownies, rice cereals, scrambled eggs, macaroni and cheese, stews, along with apple ciders began getting more preference. Later during the 70’s the crew on board the Skylab mission was even provided with tables to sit down on and enjoy their meals together.
Food grown in space
Growing food grains or crops in space is not an easy task since the atmosphere is very different from what it is on Earth. Space is not a conducive environment to grow plants for consumption, yet a group of astronauts cultivated their own vegetables and ate them too. The astronauts of the Expedition 44 mission on board the International Space Station were successful in harvesting food in microgravity, which included some leafy vegetables.
The first space-grown vegetable was the red variety of lettuce, which the crew members cleaned with citric-based sanitized wipes before consuming it. Produced under the Veggie plant growth system, astronauts harvested half of the red and green lettuces, along with mustard, which they ate as salads. These crops were collected by a technique called cut-and-come-again harvesting, which allows the crew to reap more of the same plant after it grows again.

Photo of the first Zinnia flower in space. (NASA / Wikimedia Commons)
On the ISS, a special unit is dedicated entirely for growing plants, where in the near future, astronauts would be able to grow food for consumption as well as pursue gardening activities for recreational purposes. These space plants grow under red, blue, white and green LED lights in a fully-enclosed, environmentally-controlled chamber. This secure chamber allows the crops to grow in an almost natural surrounding with the correct amount of oxygen, moisture and right kind of temperature. If the Veggie system goes as planned, NASA hopes to broaden the spectrum, by adding a variety of foods that can be grown in space. Work on wheat, cabbage and a few fruits is already underway, as space travellers get to eat their test crops.

Plants growing in Veggie unit on ISS. (NASA / Wikimedia Commons)
When an astronaut smuggled food in space

Astronauts posing with a hamburger and tomato in space. (NASA)
Although the meals provided to the space travelers have come a long way, with many improvements made in the last five decades, there was one astronaut, who would have caused a major catastrophe for being disobedient. NASA’s second human spaceflight named the Gemini Project was underway in 1962 and John Young, an aeronautical engineer and test pilot, who later went on to become the Commander of Apollo 16 mission and also the ninth person to walk on the surface of the moon, smuggled a corned beef sandwich in space.
During his four-hour-long journey, he along with his colleague Gus Grissom were provided foods in plastic bags to consume. Not happy with the quality and taste of the freeze-dried space food, Young hid a sandwich in his spacesuit from a restaurant, which he later pulled out in space to eat only to realize what a huge mistake he had made. The crumbs of bread began floating in the space shuttle and there was a risk of those getting wedged between vents or parts of the equipment that kept the spaceship up and running. Grissom and Young could have died due to a major disaster or ended up being fatally wounded. Though both the crew members remained unharmed, he was reprimanded for his careless actions.
Young passed away at the age of 87 in January 2018, but his historic stunt is still etched in the minds of people. A replica of his corned beef sandwich remains preserved in the resin at the Grissom Memorial Museum in memory of the sandwich scandal in space.
A lot has already been done in the field of aeronautics and a lot more has to be accomplished; but the procedure of sending food in outer space remains the same with possibly a few changes being made in the quality, quantity and variety of foods that astronauts can enjoy in the confines of their space shuttle, thousands of miles away from their planet.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “A Glimpse into the Exciting World of Space Tourism“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Space Food: What Do Astronauts Eat Outside the Earth’s Atmosphere? appeared first on .
]]>The post Space Debris: The Growing Hazard of Man-Made Debris in Space appeared first on .
]]>
An illustration of space debris. (David.Shikomba / Wikimedia Commons)
Space debris is debris that occurs 250 to 36,000 km above the Earth’s surface and which orbits around the Earth. It is also known as space trash, space or orbital debris, space junk, or space litter. There are two types of space garbage: natural and artificial. Natural space garbage is the dust and fragments left by meteorites, asteroids, and comets. Artificial space garbage is pieces of man-made objects. Usually, when we talk about space garbage, it is in reference to artificial garbage. There is apparently 7,500-ton of it in space.
Garbage in space
Most of the space garbage floating in space consists of non-functional satellites, sent rocket stages, fragments from the disintegration and collisions of satellites and rockets, and other mission-related debris. Since 1957, many countries have launched more than 8,000 satellites, and, of these, only about 1,900 are still operational.
The satellite management ground control can slow some of the discarded satellites in lower orbits. After slowing, these satellites fall out of orbit into the earth’s atmosphere and burn up. Some satellites may remain in orbit for decades while others may disintegrate into fragments after exploding due to leakage of the remaining fuel. Another cause of satellite breakage is the collision of the satellite with other satellites and with rockets. Meteorite strikes can also destroy satellites.

1998: Photo of a thermal blanket in orbit taken during Space Shuttle mission STS-88. (NASA / STS088-724-66)
The extreme ultraviolet radiation and the impact of microparticles in space erode the surfaces of space objects, creating minuscule fragments of debris. There is debris such as metal particles from solid rocket-motor firings, droplets of reactor coolant liquid from ejected reactor cores from decommissioned satellites, and thin copper wires from radio communication experiments and anti-satellite weapon testing. Space debris also consists of tools and stuff that astronauts lost while doing repair work on the International Space Station.
The space debris varies in size from micrometre-sized particles to fragments weighing tons. Various government agencies have space surveillance programs that track over 22,000 objects of varying sizes from 5 centimetres in diameter in low Earth orbit to about 1 meter in geosynchronous orbit. However, there are too many, possibly millions of pieces, and it is not feasible to track all of these.
Travelling at high speeds of over 17,000 miles per hour, even small pieces of debris can be catastrophic to satellites, spacecraft and space station.
Space garbage and space collisions
To avoid colliding with the debris floating about in space, most satellites and space shuttles must carry out collision avoidance manoeuvres. These are expensive both in terms of fuel usage and time requirement, and constant manoeuvring reduces the lifetime of the spacecraft. Also, the spacecraft can manoeuvre and avoid only the debris that is being tracked. It is not possible to track and avoid the rest of the space debris, given that it exists in such large amounts. The viable option is to avoid mid-sized to large debris that can potentially damage and destroy the spacecraft.
Since many countries are launching satellites and space vehicles at a rapid rate, the chances of space collisions are increasing. The debris created by these collisions will cause further collisions. If this continues, the Earth’s orbit may become littered with fragments and as a result may very soon become impassable. To prevent such a scenario, it is essential that countries with space programs create international regulations aimed at limiting space debris.
At present, various government space centres, universities, aerospace companies, and other groups are carrying out research to find workable ways of handling the space debris problem. They compile detailed data on the size, shape, and location of the debris. In addition, they gather information on reducing the creation of more debris and on removing as much of the existing debris as is possible.
Using Whipple shields to protect spacecraft from colliding particles
To protect spacecraft from the unavoidable bombardment of small high-velocity particles, the outer surfaces of spacecraft are covered with meteor bumpers called Whipple shields. These shields are made of aluminium, woven ceramic fibres, or multi-layer flexible fabric. When the striking particles collide with the spacecraft, the Whipple shields vaporize the particles into plasma. While the plasma may quickly spread over the spacecraft surface, it is too diffused to cause any real harm to the spacecraft.
Preventing fuel explosions in space
It is possible to prevent the random explosions from discarded upper stage rockets by slowly depleting the unused fuel. The prevention of these explosions reduces the creation of more fragments. However, all rockets do not have the fuel depletion technology built-in.
Reducing the creation of space debris
A space debris removal technique under consideration by the UK-based Surrey Satellite Technology and Airbus is deploying a satellite with nets or harpoons to catch the debris. The deployed satellite, known as RemoveDEBRIS, will drag the snagged debris low enough so that it can burn up harmlessly in the earth’s atmosphere. The European Commission and 10 countries are jointly funding this program for an estimated cost of $18.5 million. If the program works, the next step is launching the $400 million e.deborbit mission in 2024 to get rid of the Envisat spacecraft.

Artistic impression of RemoveDEBRIS in action. (ESA / 290476)
Researchers are in the process of developing a technique which will allow a spacecraft to collect debris into its flexible plastic body and then ferry the collected debris back to earth.
With these techniques, it will be possible to eliminate the large sized debris in low-Earth orbit. Removing the smaller bits in entirety, however, is likely to be technologically very challenging and, perhaps, even impossible.

A RemoveDEBRIS satellite by NanoRacks after being deployed. (NASA Image: ISS056E025423)
The biggest challenge in eliminating space garbage, however, is not so much technological as political. All the countries that currently have space programs would have to cooperate to provide enough funds for the space garbage disposal technology and the debris removal program. They would also have to work jointly to organize, implement, and administer the debris removal program. In addition to government programs, there are now increasing numbers of privately-owned space exploration companies. These can be incentivized to contribute to the space debris removal programs.
It will not be possible to eliminate the space garbage problem entirely, but mitigating it to a large extent could be done. Removing a large amount of hazardous waste would make it safer to launch and maintain satellites and would also make space travel safer than it is at present.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Truth Behind The Black Knight Satellite Conspiracy Theory“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Space Debris: The Growing Hazard of Man-Made Debris in Space appeared first on .
]]>The post Skylab: The Space Station that Failed in Spite of Brilliant Conception and Brave Execution appeared first on .
]]>
Skylab space station. (NASA)

Wernher von Braun. (NASA)
If well-begun means half done, shoddy beginning implies poor result. And that’s what happened with Skylab, America’s first and last space station. The idea of a midway stopover in space missions to the moon and other celestial bodies came from the German-American Scientist Wernher von Braun in the 1950s. The idea found expression in a hugely popular Hollywood movie ‘2001: A Space Odyssey’, released in 1968. The cold war to dominate earth’s outer space, unfortunately, compelled President John F. Kennedy for straight-to-moon- mission rather than work on a protracted project of the space station. Hence the trust in Apollo program. Yet Skylab remained on the back burner, to be picked up in the future. It indeed was picked up, but only to be closed down for good.
The concept was cornered by cold war considerations
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), to begin with, deliberated that space station should be created in space itself. The empty fuel tank of the old and spent space craft floating in space could be converted into a fully staffed and equipped research lab.
The idea was given up to give priority to military reconnaissance over space research. With man landing on the moon in 1969, budgetary constraints propped up. The incumbent President Richard M. Nixon curtailed NASA’s space program. Only one space station, the Skylab, was given a go-ahead signal.
A multitasking behemoth
Skylab, a prefabricated laboratory, weighing 170,000 pounds (heaviest spacecraft till date) consisted of 4 major parts: 1. The Orbital Workshop (OSW), 2. The Airlock Module (AM), 3. The Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) and 4. The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM). OWS was the main living compartment of the crew. It was supplied with 12.4 kW of electrical power by 2 large solar plates attached to it. AM helped cosmonauts walk in space. MDA carried docking port for the Apollo spacecraft and experiment package of earth resources. ATM carried Telescopes and solar plates for supplementary power.
Diagram of Skylab and its components. (NASA)

Inside Skylab Orbital Workshop. (NASA)
Running into trouble soon after takeoff
Skylab was put into space by the launch vehicle, Saturn V on May 14th, 1973. Just 63 seconds into the air post blast off, the first problem cropped up. Micrometeoroid shield, the protective cover and the thermal insulation of Skylab, came off. One of the two solar panels too broke loose. Nevertheless, the Skylab was ferried to space and put into orbit within 10 minutes of the takeoff.
Herculean efforts were made to repair the damage
As programmed by the mission control, solar plates/assemblies and ATM were set in order. However, in OWS, these assemblies were unkempt and could generate only 25 watts of power. Thermal protection already crippled with the ripping of micrometeoroids, temperature inside the lab rose alarmingly. Shorn of required electric power and temperature-control, Skylab was heading for disaster. Initial damage control efforts either restored the power, or the temperature; not both simultaneously. Luckily, the problem was solved with a workable compromise.
In view of the impaired status of Skylab, now orbiting the earth, visit of the first crew to it was deferred by 10 days. The 3-man crew comprising of Charles ‘Pete’ Conrad (commander), Paul J. Weitz (Pilot) and Joseph P. Kerwin (Science Pilot) geared-up to make the Skylab fit and functional. They carried an improvised thermoregulatory system and installed it in the lab.
Installing the system was an act of daring spacewalk; a laudable achievement indeed. Marshal Space Flight Centre, Huntsville, and Johnson Space Centre, Houston, worked in tandem with the crew. Micrometeoroid shields, ostensibly, were damaged by supersonic air currents. The scientists felt that more should have been done for the aerodynamics of Skylab before its launch. It was a daring spacewalk and laudable achievement.
Visiting crew enjoyed their space jaunt but work suffered
Skylab workshop, orbiting in space, was visited by 3 different space flights, each carrying 3-men crew. Visiting astronauts were veterans as well as rookies. They spent 171 days and 13 hours in the lab conducting hundreds of experiments on subjects including human adaptability to zero gravity, solar energy and resources on earth. A record stay of 84 days in orbit was achieved by the third crew.
Life on Skylab was easier than what popular perception may hold for space travellers. Astronauts could eat, drink, bathe and attend to call of nature with the same felicity as on earth. They dressed in casuals and worked on exercise equipment for fitness. But there was a flip side too. The last crew was all-rookie and didn’t jell with mission control. The work targets couldn’t be achieved as zero gravity proved more cumbersome than anticipated. The misunderstanding reached to the point of no communication, which was widely perceived as the incumbent astronauts going on strike.

NASA astronaut Jack R. Lousma taking shower in Skylab. (NASA)

Ergometer bicycle for exercise in the Orbital Workshop. (NASA / 7030269)
What led to the perception that the 3rd Crew of Astronauts was on (space) strike?
A 90-minute no-response from 3 rookie astronauts to the Mission Control in Texas on December 28, 1973, led to hullabaloo in NASA. Were the astronauts defying command, and resorting to strike in space?
Not really, as transpired that no-response was on account of a technical glitch because just as the Skylab completed a circle around the earth, communication Astronauts was re-established. The 90 minute disconnect on that fateful day, said one Astronaut on board, was an unintended technical error on their part.
Apart from technical problems time and again, the crew was clearly ill at ease with mission control on earth. Their discomfiture began on the very first day of their arrival on Skylab. They found mannequins carrying their nameplates, a way of their predecessor, Skylab 3 crew, pranking them. Add to this the huge workload assigned to them, as it would be the last lap of Skylab mission, and the mental pressure on the rookie crew can be understood.

Mannequins left by the Skylab 3 crew of Skylab to be discovered by the Skylab 4 crew. (NASA)
The crew, unlike other missions, had no space-veteran. It was snubbed time and again, and denied encouragement and feedback by the mission control. Work overload seemed a natural reaction of NASA as the mission was supposed to be called off shortly, and the mission control wanted to draw maximum work from the men in space. The crew worked overtime to their threshold capacity. Their dress and accessory were a misfit and the irritation showed in their body language. Their bosses construed it as indiscipline and called them lazy and careless. That, surely, heightened misunderstanding. By no stretch of imagination was it a ‘strike in space’, as the very idea of such strike was untenable and foolhardy. NASA too finally relented that the Astronauts were indeed overworked and stressed out.
Falling Skylab created commotion all over the world
The consistent efforts of NASA notwithstanding, Skylab suffered delays and derelictions. Nature too seemed unfriendly. The hot and expanding atmosphere messed with lab’s orbit around the earth. Scientists anticipated putting Skylab into a higher orbit. But doing so would take time, and the lab had already tipped to fall on earth by 1979. That put a stop to prospective salvage operations, and the people world over waited for the fall with fear and anxiety.
The D day arrived on 11th July 1979. The debris of Skylab fell over the Indian Ocean and Western Australia. There were fears that it could fall in South India. There were reports of people sporting a metallic hat to guard against the debris of the free-falling Skylab. Tragicomic reports of people hurrying up with their important assignments, well before the lab could come in their way, appeared in newspapers. Thankfully, the falling of Skylab didn’t harm any life or property on earth.
Skylab project surely didn’t end on a planned and positive note, yet the repertoire of knowledge and space experience it generated can’t be ignored. Especially so because the project parried several cliff hanger situations in spite of the low downs of the budget and the human resource.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “A Glimpse into the Exciting World of Space Tourism“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected]
RELATED
The post Skylab: The Space Station that Failed in Spite of Brilliant Conception and Brave Execution appeared first on .
]]>The post NASA’s Deep Space Network: How We Communicate with Space Probes Billions of Miles from Earth appeared first on .
]]>
Deep Space Network: An antenna at Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex. (NASA / JPL-Caltech)
The Deep Space Network or DSN is a network of radio antennae, owned by American Space Agency NASA and in particular, a division of theirs called the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). Spread across three continents, the DSN antennas act as middlemen to transfer data between spacecraft from Outer Space interplanetary missions as well as other satellites which orbit Earth.
History of Deep Space Network
1963 brought about the launch of the DSN under the JPL which was originally an institution of the U.S Army. They used it for mapping and reconnaissance. NASA saw great value in the program and had it transferred when the opportunity arose, knowing that an isolated hub for communications would be more effective than each craft or mission having to create its own. The Californian location was made headquarters, with Canberra joining the program in 1965 and Madrid later in the same year. At this time it serviced only three crafts yet just half a century later the number had increased to thirty-three. This includes vessels from organisations outside NASA including the European Space Agency, Japanese Space Agency and their Indian counterpart.
The sites of DSN
At any given DSN site there are four antennas. Each site sits 120 degrees apart in longitude, in Canberra (Australia), Madrid, (Spain) and in Goldstone, (California). They are evenly spaced meaning that the rotation of Earth will not affect signals as it disappears under the horizon. In this regard, one might say that the sun never sets on NASA’s empire.

Deep Space Communications Complex in Canberra, Australia. (NASA / JPL-Caltech)
They are situated on Earth as a means of space saving. They are too large and too heavy to be usefully implemented on spacecraft which traditionally only have small devices. They also deliver weak signals back to Earth but it is a secure delivery. The strength of signal the antennas receive is ridiculously low,
“…20 billion times weaker than the power level in a modern digital wristwatch battery.”
It is still effective in receiving data none-the-less. Once the DSN centers receive the data they send it to the Operations Facility at the JPL, In Pasadena, California. Then the data is processed and the pictures come to life.

1993 photo of Deep Space Network Operations Center at JPL in Pasadena, California. (NASA / JPL-Caltech)
Deep Space Network antenna
According to the DSN website, they are “…the largest and most sensitive scientific telecommunications system in the world.” Their goal is to “…improve our understanding of the solar system and the larger universe.” They provide the crucial connection for commanding our spacecraft and receiving their never before seen images and scientific information on Earth, propelling our understanding of the universe, our solar system and ultimately, our place within it.
Most correspondence is among the Voyager missions. Both set off in 1977 to monitor planets inside our solar system with Voyager II launching 16 days before Voyager I. At the time of writing, both have made it outside of the solar system – monumentally the only two crafts in history to do so. Exactly what this means,
“For the second time in history, a human-made object has reached the space between the stars. NASA’s Voyager 2 probe now has exited the heliosphere – the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun.”
To give a glimpse of the important of DSN, here are some of their accomplishments. They provided the images of Neil Armstrong’s moonwalk, helped in the rescue of the Apollo 13 astronauts when they couldn’t access the main communications sector of NASA. 1965 brought the first close up images of Mars, 1974 – Mercury and in later years: Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune as well as their rings and moons. And of course the Voyager missions, which have documented their maiden move into interstellar space.
Amazing facts about Voyager
“Launch: Voyager 2 launched on August 20, 1977, from Cape Canaveral, Florida aboard a Titan-Centaur rocket. On September 5, Voyager 1 launched, also from Cape Canaveral aboard a Titan-Centaur rocket.
Between them, Voyager 1 and 2 explored all the giant planets of our outer solar system, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune; 48 of their moons; and the unique system of rings and magnetic fields those planets possess.”
Both Voyagers carry The Golden Record which we have spoken about before.
Problems with Deep Space Network
Alas, not all is sweetness and star-light with DSL. There have been mistakes made which it would seem are inevitable in such a complicated type of environment and distance. However, a prestigious organisation such as NASA strives to make sure that errors do not happen as the cost can be extreme as well as time-consuming to find and bring a replacement.
One example is of Cassini, a spacecraft which was orbiting Saturn’s equator and planned to move into the atmosphere after thirteen years dancing around the rings. When the time came, the uplink from DSL failed and so Cassini was unable to make the plunge which had to be done in a certain moment for favorable conditions. The dive was made a day later but it showed a chink in the seemingly impenetrable armour of DSL.
It is not the first fault made by DSL and while some criticisms have been admonished it retains support from many major players in the astronomy game. For example, astronomer Brad Peterson states, “As NASA launches increasingly complex and data-hungry missions… the need for DSN is only going to increase.”
Upgrades have been made to keep the technology ticking over and eliminate errors yet it is said that the recent blips actually occurred because of the newest antenna installed. None-the-less, DSL have never dropped below “…95% of both outbound and incoming signals, its minimum goal.” This is according to Pete Vrotsos, program manager at NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation office. And moreover, this is with reported annual budget cuts from NASA. Similar initiatives seem to be having more investment in European missions: Rosetta, Gaia and Mars from the ESA are receiving consistent support.
They are furthermore trying to implement updated techniques such as laser systems opposed to radio transmissions but this comes with its own problems. They are lighter and more energy efficient than older style systems which would help proceedings in the long run.
The future of DSN
Investing money in ventures like this is a controversial topic. Many will say why not invest in our planet instead of planning wild goose chases into the dark unknown. The counter of that would be to reprise the famous Oscar Wilde quote,
“We are all in the gutter but some of us are looking to the stars.”
Millions of years of nomadic culture mean that the human race is destined to explore and so space missions will forever be part of the fabric of life. Outward thinking and exploring space is an unexplainable necessity. We believe that Outer Space has the key to solving many problems on Earth but we just don’t know where to look. For this reason, NASA’s DSL program is a much-needed commodity, one which can hopefully get through this apparent time of austerity and conquer the test of time.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Did Man Really Land on Moon? The Dilemma of Apollo 11’s Missing Tapes“.
Official Website:
Real-time status of communications with NASA’s deep space explorers
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post NASA’s Deep Space Network: How We Communicate with Space Probes Billions of Miles from Earth appeared first on .
]]>The post Sex in Space – Is It Possible? and Why It is Important appeared first on .
]]>
Astronaut Jan Davis and Mark Lee, the only married couple to have travelled together in outer space. (The U.S. National Archives)
Sex of course, needs no introduction. A fundamental building block of life and evolution as well as a popular past-time would be extreme understatements. It is inherent in the human genus and more and more everyday plays a large role in all aspects in the fabric of life – advertising, movies, and nightlife etc. For this reason, we assume that people are having sex everywhere: houses, hotels, colleges, beaches, farms, roller coasters, boats and hot-air balloons. One would expect in spaceships and stations also, but it turns out that it’s not so easy to have Outer Space intercourse.
According to NASA,
“Former and current astronauts don’t like to talk about space-shuttle sex, and NASA says that if it’s ever happened, the agency doesn’t know anything about it. (NASA has never conducted official experiments on animal reproduction in space, says a spokesman.)”
This was back in 2007 but explains the lack of practice or even consideration before that year. It is more and more becoming a necessary topic to discuss as plans to colonise other planets and space has entered the goals of the human race. NASA officially began preparatory missions in 2009 but presumably had feelers out way before then along with other organisations and personnel.
Many would agree, that NASA is simply reserved about making information like this public. For example scientific writer Pierre Kohler,
“The issue of sex in space is a serious one… The experiments carried out so far relate to missions planned for married couples on the future International Space Station, the successor to Mir. Scientists need to know how far sexual relations are possible without gravity.”
The problem with Sex in Space
The primary problem with intercourse in space arises from weightlessness and factors from Newton’s Third Law which means an easy process on Earth is much more difficult in space. For every reaction, there is an equal and opposite reaction but not when something is connected.
This is universal law so it remains the same anywhere in the universe. It means that if the couple remain attached they will not be able to exert force upon one another and unless there is another object to counter, their velocity cannot change. Along with this, anti-gravity prohibits any real movement, however slight. All our evolution has all taken place under Earth’s atmosphere and conditions, in space means a completely new environment for our bodies to process. Gravity has a hand in a number of our functions from the basic principles of cells and organs so we cannot just use a device which creates gravity. Beyond that, pregnancy and birth could cause problems in other environments so difficulty with conception initially may not be a bad thing – like a warning from nature. Scientists have already tried it with rats and while they were able to breed, the litter were unable to survive long.
Lack of gravity can cause a lot of problems if a person is expending too much energy, extreme perspiration and nausea can occur. Muscles and bones can become extremely brittle and risk injury with the slightest mishap or accident. Circulation changes also, a pulse rate which can swell your heart and slow down circulation.
Things we take for granted in 1G – our gravitational atmosphere. Human behaviour is greatly affected also, with astronauts reporting extreme changes in mood which could cause complications in highly charged emotional situations.
Attempts
There has been nothing official from NASA and their counterparts but here are some examples of individual parties looking to complete the task. Multimillionaire astronaut Dennis Tito owns a foundation who announced a two-person crew would flyby Mars and back to Earth. The Inspiration Mars Foundation was set for a 501 day trip but it has yet to be completed.
Porn site Pornhub even plans to make a pornographic film in space – which would be the first. A crowdfunding campaign which relies on donations is called Sexploration. Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic was said to reject a $1 million offer to shoot a film, and while the company was not named it could possibly be the streaming website.

Testing 2suit in a reduced-gravity aircraft during a parabolic flight. (Steve Boxall / Wikimedia Commons)
Solutions
There have been creations to solve the problem including an invention called 2suit. A type of apparel designed by a famous astronaut and novelist Vanna Bonta which generated much publicity and discussion. A documentary described how a couple tested the suit in a zero-gravity airport yet even kissing proved a challenge and more time was reportedly needed.
The future
With more and more talk about colonising other planets, sex in space is an important topic as it is the fundamental operation needed to do so. And reaching hospitable, goldilocks planets could take generations which is why it is not just sex, but sex in the confines of a space-saving spacecraft that has to be negotiated. It is an exciting experiment for the future in terms of the logistics. That is without taking into consideration whether it is something mankind should or should not do.
From a science fiction standpoint, it is a subject which has been covered many times over. From many male perspectives, there is one scenario which could be appealing. Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins wrote a tongue-in-cheek possibility in his autobiography. Time magazine posted it,
“Imagine a spacecraft of the future, with a crew of a thousand ladies, off for Alpha Centauri, with 2,000 breasts bobbing beautifully and quivering delightfully in response to every weightless movement … and I am the commander of the craft, and it is Saturday morning and time for inspection, naturally.”
[It should be noted that author Arthur.C Clarke informed the editor of Time that he was first to write this in his novel Rendezvous with Rama (1983)]
The human race has achieved so much that sex in space will without a doubt become a mainstay, it is just a question of when.
Recommended Read:
An Astronaut’s Guide to Life on Earth | By Chris Hadfield
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Sex in Space – Is It Possible? and Why It is Important appeared first on .
]]>The post The Soyuz 11 Tragedy – The Death of Three Soviet Cosmonauts in Space appeared first on .
]]>
Photo of Soyuz 11 crew. (USSR Post / Wikimedia Commons)
Travelling to where no man has ever gone before sounds glamorous in theory, but comes fraught with all manners of dangers and even fatalities in practice. In space travel, where we are confronting the unknown, it can be difficult and even downright impossible to predict how things are going to turn out, despite the most stringent preparations. The Soyuz 11 tragedy is an example of this, and the very first instance of humans dying in space.
Soyuz 11 and the first space station in earth’s history
The Salyut 1, which the Soviet Union launched into the earth’s lower orbit on 19 April 1971, became the first space station in our planet’s history. Now all that remained was to get people on this space station. The Soviets succeeded with this as well on 7 June 1971, when the Soyuz 7k-OKS, a spacecraft designed for space station flights, docked the Soyuz 11 capsule at the space station. An earlier space mission, Soyuz 10, had docked but failed to properly latch on and the cosmonauts had therefore been unable to enter the space station.
There were three cosmonauts onboard Soyuz 11: The Commander, Georgy Dobrovolsky, the Flight Engineer, Vladislav Volkov, and the Test Engineer, Viktor Patsayev. It was a first space flight for Georgy Dobrovolsky and Viktor Patsayev, and the second for Vladislav Volkov. As it turned out, unfortunately, it was also to be the last flight for all three.
Record-setting stay at the Salyut 1 space station
Nobody had ever stayed in space on a space station, so it was a very big event when the Soyuz 11 crew not only docked successfully but also managed to latch on and enter it. They did encounter an immediate problem of a smoky interior due to a faulty ventilation system, but they soon fixed that problem. They had to retreat to their capsule and wait until the air cleared, but they were able to go into the space station and remain there after that. They stayed at the station for almost 23 days and, during this period, a large percentage of the public in the Soviet Union assiduously watched the televised broadcasts that the cosmonauts made. There was great curiosity about what it was like to live in a space station and the cheerful cosmonauts helped their audience experience it second-hand. In addition, the Pravda newspaper, the official newspaper of the Communist Party, published regular updates of the cosmonauts. They became very popular with the general public.
There were some problems at the space station, but the crew managed to deal with these. They put out a fire on the eleventh day of their stay and allayed the fears of the ground crew that they might have to abandon the station. The crew discovered that station vibrated from end to end when they used their treadmills. They postponed the launch of an N1 rocket. They remained healthy and in good spirits till the end of their stay and set the very first record for human endurance in space.
Soyuz 11’s return to earth
After what seemed to have been a very successful and illuminating space mission, everyone eagerly awaited the return of the cosmonauts. The Soyuz 11 capsule re-entered the earth’s atmosphere on 30 June 1971 and made a good landing on a flat, uninhabited plain in Kazakhstan.
The recovery team approached the capsule, which had landed on its side, and found it to be remarkably undamaged on the outside, without even a dent anywhere. They knocked on the capsule exterior, but there was no answering knock from within. Filled with foreboding, they forced open the hatch and found themselves confronting an unexpected and horrifying sight. The three cosmonauts were lying on their couches, seemingly unconscious, with blood streaming from their noses and ears and vivid blue marks on their faces. Commander Dobrovolsky’s body was still warm, which gave the rescuers some hope. They hurriedly removed all three from the capsule and performed CPR to try and revive them. It was to no avail. The three cosmonauts were already dead.
Death on the Soyuz 11
The ground crew had become concerned after losing audio contact with the cosmonauts as the Soyuz 11 capsule re-entered the earth’s atmosphere. They had come prepared for emergencies, but finding the crew dead in this manner was a shock. It seemed inexplicable too, given that the capsule was undamaged.
According to the doctors who performed the CPR, the crew had died from asphyxiation. Later, pathologists at the Burdenko Military Hospital carried out autopsies on the bodies and discovered that the cosmonauts had died from blood vessel haemorrhaging that occurred mainly in the brain, but also to an extent in the nose, ears, and skin. The haemorrhaging resulted from a sudden drop in pressure in the capsule’s interior; the blood vessels ruptured when the nitrogen and oxygen in the bloodstream bubbled from the pressure drop. The pathologists also found inordinately high amounts of lactic acid in the blood, signalling extreme stress before death occurred.
Data from the biomedical sensors on one of the cosmonauts showed that the cosmonaut had a cardiac arrest within 40 seconds of the pressure drop. The capsule’s interior pressure had dropped to zero within 15 minutes of the retrofire.
What had caused the pressure to drop though?
Cause of the decompression on the Soyuz 11
Investigators examined the capsule thoroughly to discover the cause of the decompression and finally found that it was due to the inadvertent opening of a breathing ventilation valve.
These ventilation valves were between the orbital module and descent module and the spacecraft engineers had designed them to shut automatically during descent. Alexei Leonov, the Commander of the original crew, had expressed doubts about this automatic shutting of the valves. He had advised the Soyuz 11 crew to not trust the automatic function and, instead, to close the valves manually. They had, unfortunately, either forgotten or disregarded this advice.
He had been right, it turned out. The automatic closure failed when the explosive bolts holding the orbital and descent modules fired simultaneously, instead of, as expected, firing sequentially. With the force of the simultaneous firing, the valve seal loosened and opened the valve when the capsule was at an altitude of 168 kilometres. The pressure inside the capsule dropped instantaneously. Since the position of the valve was in between the seats, the cosmonauts were unable to find and block it to prevent the air escaping from the capsule.
During the examination of the capsule after the tragic flight, Leonov tried closing the valve manually and discovered it took him up to a minute to do that. In an emergency situation, such as the one that the Soyuz 11 crew had encountered, a minute was too long.
If the cosmonauts had worn space suits, they might have survived. After the Soyuz 11 tragedy, the Soviets redesigned the Soyuz aircraft to hold only two crew members with space suits. A later redesign in 1981 allowed space for three crew members with space suits.
The funeral of the Soyuz 11 crew
The mood of the nation turned from expectant joy to sombre grieving. Nobody had expected the events to take such a tragic turn. The Soviet government organized a massive state funeral for the three cosmonauts and the burial took place in the Kremlin Wall Necropolis in the Red Square in Moscow. They later received posthumous medals as Heroes of the Soviet Union.

Soyuz 11 Memorial in Kazakhstan, built exactly where the module had been found. (Vikkom0203 / Wikimapia)
The Soviet state media did not announce the cause of their deaths until almost two years later.
The Soyuz 11 tragedy alarmed the US Americans who were preparing for their Skylab program. They assumed that the Soviet cosmonauts had died from their extended stay in a zero-gravity environment, and, of course, they did not want to risk the same thing happening to their astronauts. Charles Berry, a NASA doctor, discounted this theory. It was more likely, he said, that the cosmonauts had died from toxic inhalation. The space program authorities found this explanation more to their liking and continued with the space program.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Lost Cosmonauts of USSR: Did the Soviet Union Cover up its Secret Cosmonaut Casualties?“.
Optional Visit:
Soyuz 11 Memorial | Kazakhstan
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post The Soyuz 11 Tragedy – The Death of Three Soviet Cosmonauts in Space appeared first on .
]]>The post Ultima Thule: A Snowman-Shaped Celestial Body That is the Farthest Object a Space Probe Has Ever Captured appeared first on .
]]>
Ultima Thule. (NASA / Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory / Southwest Research Institute, National Optical Astronomy Observatory)
Space is no longer a figment of humans’ imagination. With so many new aspects being unfolded each day by space explorers and government agencies, there is hardly any scope for denial now. Space is real. And the knowledge of events and occurrences that take place millions of kilometers away from our planet are nothing but man’s tireless endeavours to find out new things that lie in darkness, well beyond our solar system. One such discovery that has come across as yet another major achievement in the field of space research is the recent photographs of ‘Ultima Thule’. A first of its kind finding, Ultima Thule is considered to be the most distant object in space to have been captured on camera by a space probe.
The New Horizons mission
The US space agency’s New Horizons Mission in accordance with John Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, was launched in the year 2006 with a view to perform the primary operation of a flyby (where a probe is sent in outer space to only fly past a planet so that it can be studied in detail) to Pluto. In a bid to research and learn more about the dwarf planet of our solar system, the probe performed its task successfully in the year 2015. The interplanetary spacecraft New Horizons was also assigned another task, which was to fly by and gather more scientific information about objects in the Kuiper Belt, farther away from the minor planet Pluto. And ringing in the New Year, the probe did send back good news after all.

New Horizons in 2005. (NASA)
What is the Kuiper Belt?
An area that belongs to our solar system, which is believed to be very frigid, lying beyond the orbit of planet Neptune, where hundreds of thousands of dwarf planets, comets, asteroids and many other small celestial bodies are contained is the Kuiper Belt. The Kuiper Belt is the icy band where the dwarf planet of Pluto was first discovered in the year 1930. Initially given the status of a planet in 1992, Pluto’s standing came under the scanner when other objects of similar sizes were discovered floating in the Kuiper Belt. Pluto’s status was then stripped of and it came to be termed as a dwarf planet ever since. Similarly, many more objects in the Kuiper Belt known as KBOs (Kuiper Belt Objects), including Ultima Thule, have been discovered in the icy ring consisting of dwarf bodies, among which the discovery of Ultima Thule is of prime importance.
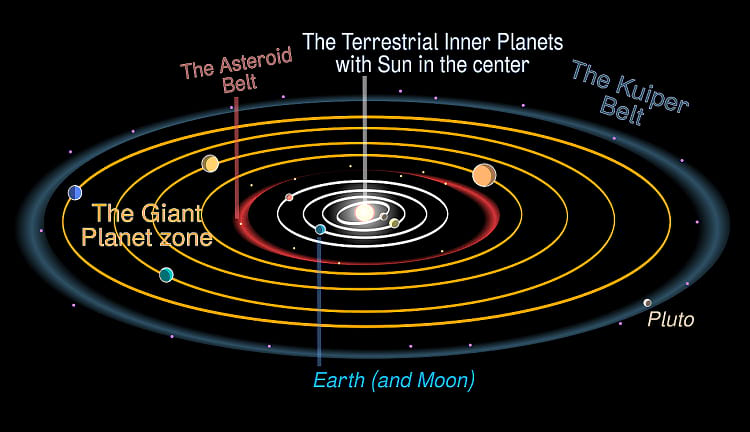
Our solar system representation with the asteroid belt and Kuiper belt. (Rursus / Wikimedia Commons)
What is Ultima Thule?
Long before New Horizons space probe made a flyby beyond Kuiper Belt’s gatekeeper Pluto, it had sent over a picture of a hazy, single dot that was named 2014 MU69. But tired of using the official designation every time, scientists immediately gave it the nickname Ultima Thule, for two reasons. Firstly, it was the ultimate discovery that a manmade spacecraft had ever come across (which explains Ultima) and secondly, during the fourth century Europe, an icy cold, mythological, distant land, lying far away in the north was termed Thule, which also stuck with the nickname of NASA’s newest finding. Out of the thirty-six names that were compiled and posted online, Ultima Thule gathered the most votes and so by majority, in 2014 MU69 came to be known as Ultima Thule.
Ultima Thule is also considered a fossil celestial body that holds the secret to the birth of our solar system. It is a trans-Neptunian object in the Kuiper Belt, which is a contact binary body, approximately 32 by 16 kilometres in dimension. It is composed of two distinctly separate objects fused together, also called lobes, which explain its contact binary nature. The two lobes of the almost spherical body might have been moving towards each other over several years until they touched and together came to be known as Ultima Thule. The larger body was named Ultima, while the smaller one was termed Thule. Scientists are also looking into the possibility that the two objects could be orbiting each other.

Formation of Ultima Thule. (NASA / JHUAPL / SwRI / James Tuttle Keane)
As per NASA’s data, the picture of Ultima Thule resembles a huge snowman adrift in space; of which, the duration of rotation period is yet to be ascertained correctly. The larger body is three times the size of the smaller body and its brightness did not change as it made a rotation. Ultima Thule spins end to end like a propeller and its axis was found to be pointing outwards. Like most other dwarf planets and regular ones, Ultima Thule has been found to be moderately cratered. The newly found celestial object is considered to be an icy world that is some 6.5 billion kilometers away from the Earth. It is believed to be a building block of planets and its study might offer clues into how the Earth, its neighbouring planets and the solar system formed in the first place.

Artistic impression of a non-contact version of Ultima Thule. (NASA)
As per a statement issued by the lead scientist of the mission Dr. Alan Stern, the probe will travel behind the Sun, the outer surface of which will interfere with the transmission of photographs back to the Earth. It takes around six hours one way for data to be sent back to the Earth, which is why more information can only be relayed back on January 10, once the link to the spacecraft is restored.
First discovered by astronomers through the Hubble Space Telescope on June 26, 2014, Ultima Thule became clearer as New Horizons spacecraft made a flyby beyond Neptune in the solar system and then went further past Pluto into the Kuiper Belt on January 1, 2019.
Now scientists are keeping a close watch on this newly-discovered object in space and waiting for more information to be transmitted from the New Horizons spacecraft in a bid to find out more not just about the happy snowman Ultima Thule but also about the formation of planets inside the solar system and outside ones contained within the Kuiper Belt. It is only a matter of time before we get to know more about the farthest object in space that man has ever literally laid his eyes on.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “HP Enterprise Creates History as Cloud Computing Experience Reaches Space“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Ultima Thule: A Snowman-Shaped Celestial Body That is the Farthest Object a Space Probe Has Ever Captured appeared first on .
]]>The post What are Minor Planets and Dwarf Planets? appeared first on .
]]>
Ceres, dwarf planet. (Justin Cowart / Ceres – RC3 – Haulani Crater)
All through a major portion in the elaborate and intricate realms of history, astronomers, stargazers and celestial object experts have put their extensive focus on the principal stellar bodies like the Sun, Moon, Planets and Comets. They happened to be the extraterrestrial objects located in the easy nearness to Earth and were effortlessly spotted in the sky.
With gradual advancements in technology and research, other intriguing objects hovering around the solar system came into the limelight. They were anything but planets, comets or moons. They were small and compact objects orbiting in a plain-sailing manner amid the cosmos. They came to be known as “minor planets”.
What is a minor planet?
A minor planet is a celestial object that revolves around the Sun and does not fall into the category of either a planet or a comet. The origin of the term minor planet dates back to the 1800s. Several other nomenclatures like asteroids and planetoids have been used in a perplexing blend with minor planets.
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) committee made this situation even more complicated when they came up with another round of classification with the inclusion of more celestial bodies like “dwarf planets” and “small solar system bodies”. Simultaneously the IAU redefined the planet with amendments and Pluto was demoted to the rank of a dwarf planet.
The scientists from IAU assert that it is hydrostatic equilibrium which measures the capacity of a heavenly object to maintain a nearly spherical shape. It is also this distinctive feature that differentiates dwarf planets from the asymmetrically outlined small solar system bodies.
The labelling adds to further confusion as the IAU still maintains to recognise and use the term minor planet. Thus to be branded as a dwarf planet, the heavenly object should have enough mass to mould itself into a spherical form through a gravitational pull.
How are minor planets grouped?
Minor planets can be classified into several major categories namely asteroids, Trans-Neptunian objects, Trojans and centaurs. The asteroids reside within the asteroid belt which is the spatial territory between Mars and Jupiter. Astronomical bodies which are found to be orbiting beyond Neptune fall into the Trans-Neptunian class. Trojan is also a minor planet that ideally co-orbits with a planet or a moon and keeps up a stable and steady axial position at a definite place in relation to the larger object. And finally, centaurs are stellar objects that rotate in unsteady orbits between Jupiter and Neptune.
Minor planets are commonly prevalent orbiting at their own pace within the boundless expanse of the solar system. As of 2018, nearly 757626 minor planets have been identified and registered, 516386 have been officially numbered and 21264 minor planets have formal names.
Ceres – the smallest dwarf planet
Ceres is one of the dwarf planets and is the only celestial body of its kind to be situated within the innermost ranges of the solar system. The other siblings of Ceres are located on the exterior peripheries inside the Kuiper Belt (the extraterrestrial region beyond the orbit of Neptune). Although Ceres is considered to be the smallest of all the discovered dwarf planets, it is the biggest entity within the asteroid belt. Ceres is devoid of any resident moons.

Our solar system representation with the asteroid belt and Kuiper belt. (Rursus / Wikimedia Commons)
Discovery and early history of Ceres
Sometime in the latter half of the 18th century, some astronomers predicted the mere existence of a tiny planet between Mars and Jupiter through mathematical computations. On 1st January 1801, Giuseppe Piazzi, a Sicilian astronomer stumbled on what was then used to be appraised as a planet. It was named Ceres after the Roman deity of corn cultivation and harvests.
Although Ceres was downgraded to an asteroid years later because of its minuscule size and unworthy gravitational features, in 2006, Ceres was again promoted and it attained the ranking of a dwarf planet. It could not touch the full planetary status as it failed in clearing its surrounding debris through gravitational effects. However, it is oftentimes categorised as an asteroid as well.
Being the largest asteroid and the smallest dwarf planet, the expanse of Ceres is a paltry 590 miles. The radius of Ceres is 296 miles. The duration of a typical day in Ceres is 9 Earth-hours. The planet takes 1,682 Earth-days or 4.6 Earth-years to complete one revolution around the sun.
The marked nearness and tiny mass have prompted a few scientists to recommend Ceres as a prospective serving site for operated landings and a launch pad for the profound utilization of space missions.

What is a Dwarf Planet? (Jelly / NASA / JPL-Caltech)
Ceres is an oblate spheroid just like Earth
Ceres has the distinctive shape of an oblate spheroid unlike most of the different rocky objects existing in the asteroid belt. Ceres also has a convoluted protrusion all over its equator. Researchers profess that Ceres also has a lodged ocean and an intrinsic wafer-thin atmosphere primarily formed of water vapour.
The water vapour supposedly gets generated either by ice volcanoes or by ice in the vicinity of the sublimating surface when a conversion from solid to gaseous form takes place. The latest findings have uncovered some of the underlying facts about Ceres. However, many other secrets still lie unravelled.
All about luminous spots and lonesome mountains
A total number of 130 identical spots of wavering brilliance were found on the planet’s surface. Ceres has an inherent reflective surface that reminds of layers of fresh asphalt. The luminance of the spots varied from anything between the dull and dreary to the sparkle and shine. The most irradiant portion, called the Occator Crater, having a width of almost 56 miles, houses the most prominent and stunning assembly of beaming spots on the celestial surface.

Occator Crater on Ceres. (NASA / JPL-Caltech / UCLA / MPS / DLR / IDA / PSI)
Initial conjectures centering on the spots hinted at the probability of the existence of ice volcanoes covering large-scale portions of the dwarf planet. However, Dawn’s probe unearthed a solitary and lonely mountain shooting directly upwards from the surface. The mountain takes the contour of a pyramid and has an altitude of 6,437 metres. The mountain surprisingly exhibits no sign of any volcanic or geological activity that could at least offer some clues about its origin.
Ceres is found to contain hydrated minerals carrying ammonia, carbonates, water, ice and the recently revealed organic specimens. Therefore, this fresh finding suggests that Ceres has all the indispensable components to generate and preserve life.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Gliese 581g: A Habitable Exoplanet or Just Another Celestial Object Orbiting a Star?“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post What are Minor Planets and Dwarf Planets? appeared first on .
]]>The post HP Enterprise Creates History as Cloud Computing Experience Reaches Space appeared first on .
]]>
The International Space Station. (NASA / Crew of STS-132)
Everyone is aware of a vast, limitless zone, several hundred kilometers outside the Earth’s atmosphere, where celestial objects orbit around giant stars and many unknown astronomical events take place. This boundless zone, known as space, is intriguing and there have been a host of government bodies and individual agencies that have spent billions in research and exploration of this area of nothingness. And to add to it all, there’s one major recent feat in the field of computing that a private info-tech company has achieved, which will change the way astronauts transmit their data back to the Earth. But before we get there, here are a few basics we must know of first.
What is the International Space Station?
In simple terms, the International Space Station (ISS) is a home away from home. It is a huge spacecraft orbiting the Earth, where astronauts live and carry out scientific researches for specific periods of time. Launched in the year 1998 by a Russian rocket, the International Space Station was built by a group of nations, where the first crew, comprising of astronauts from different countries of the world, arrived in the year 2000. Over a period of time, more nations added their own modules to the space station, finally making the ISS as big as an entire football field, as we know it today.
Weighing approximately half a million kilograms, the ISS is huge enough to accommodate six astronauts at a time, with all necessary living facilities, which also includes a gymnasium. With research labs from countries like Japan, USA, Russia as well as some European nations including Germany, France and The Netherlands; the ISS is where space research and exploration is carried out, which otherwise could not have been done on the Earth.
What is Cloud Computing?
We all know that a computer is a device that receives information, processes it; stores it and recalls it as and when instructions are fed into it. A remote server is a computing term, which is a device that is not attached to the client’s keyboard but it can be accessed from any part of the world from anywhere over a shared network. And cloud computing is a term, which means the delivery of a host of Internet services like databases, applications, networking, analytics and storage to a client on demand in any part of the world. In short, cloud computing means a shared pool of computer resources and services, which can be accessed remotely over the Internet by a lot of clients.
Cloud Computing and International Space Station
In the year 2017, when a space cargo capsule called SpaceX Dragon was sent into orbit to deliver cargo to the astronauts at ISS, little did the space researchers know that they were in for a pleasant surprise. Developed by tech giant Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), a supercomputer known as Spaceborne Computer was delivered to the International Space Station after it was thoroughly tested for over a year to check if it would sustain in outer space. The supercomputer (a network of computers working together) was examined to see if it could withstand the harsh space atmospheres, radiation flares, frequent power outages, zero gravity and vacuum; and only then it was delivered to its destination aboard the ISS in August.
Basically, the idea behind delivering this supercomputer to the ISS was to cut down on time that the astronauts required to send research data to and fro from space. HP Enterprise developed cloud computing techniques in Spaceborne Computer and made it easier for the experimenters in orbit to store their own data and use it when necessary. Till now, astronauts transmitted data back to the Earth first to get it checked, while waiting for results to come back. Now, researchers can directly run their analyses in space instead of sending it back for insight. And so, with the help of cloud computing, communication between Earth and space can become a lot quicker, more real-time and much more efficient.
How cloud computing could ease challenges at the ISS
The connection and bandwidth between space and Earth is slow and intermittent and there could be problems regarding communication for a few minutes. With cloud computing, the unreliability can be done away with and there can be no chances of data loss, while it is being sent back to the Earth, as opposed to before. Testing supercomputers in space can make way for more research studies on an advanced level in the future, where astronauts are eyeing other planets for habitation such as Mars. The Spaceborne Computer will also help scientists to carry out their research work without making use of bulky, overly expensive and time-consuming computing devices.
As the one-of-a-kind, first-ever cloud experience, which is set to make communication between Earth and space easier, makes its way into the International Space Station; it gives us one more reason to rejoice, as mankind takes another giant leap in the field of space communication.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “NASA’s Deep Space Network: How We Communicate with Space Probes Billions of Miles from Earth“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post HP Enterprise Creates History as Cloud Computing Experience Reaches Space appeared first on .
]]>The post Did Man Really Land on Moon? The Dilemma of Apollo 11’s Missing Tapes appeared first on .
]]>
Apollo 11 slow scan television photo. (NASA)
When the first human, Neil Armstrong, walked on the moon on 21st July 1969, America as a nation was facing multiple challenges on several fronts. With more than 15 thousand soldiers killed, over a lakh wounded, and 5 lakh soldiers deserting US army till 1973, anti-Vietnam-war sentiments were at a peak. Credibility, as well as the Economy of American state, was in bad shape.
A domino effect, NASA began to dismantle ALSEP’s (Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package) network of Scientists and Engineers in 1974. By 1977 there was a total shutdown of stations receiving radio data from lunar instruments put on the moon by Apollo missions. But an exploration of the moon was too significant to be stalled abruptly. The body of knowledge it created required refining and updating for space research.
Apollo 11’s missing tapes
Dr. Marcus. G. Langseth, Scientist at Columbia University had studied the flow of heat through Earth’s upper layer between 1966 and 1975. Seiichi Nagihara, a geophysicist at Texas Tech University wanted to analyse Langseth’s data with upscale analytical techniques which were not available in Langseth’s time. But he was shocked to find that half of the ALSEP data was lost following project shut down. Search for the missing files being a top priority; two dozen scientists joined him and formed ‘ALSEP Data Recovery Focus Group’ in 2010. The Group, funded and supported by NASA, recovered 450 tapes at National Records Centre in Maryland. But 4550 archival tapes, which would go bad in a decade’s time, remained untraced giving agonists fodder for calling the moon missions a hoax.
Impact of the missing tapes
Rumour Mills worked overtime, right since the day Neil Armstrong walked on the moon, to say that no man ever landed on the moon. What was flashed on television worldwide, they said, was a film made in a studio. Those who couldn’t send even a chimp into space in 1961, argued wags, now claim 2 men have landed on the moon; how come? Where has the huge $25 billion Apollo budget gone? Bickering found a base in a book “We never went to the moon: America’s $30 billion swindles” self-published in 1974.
Author, Bill Kaysing said Apollo program was a subterfuge for the secret militarization of space by America and that moonwalk was stage show passed as space odyssey. Author’s association with Atlas V (a rocket used for interplanetary missions and military payloads to International Space Station) gave him some credibility but the book had little in the name of scientific approach and investigative journalism.
Another sceptic, Bart Winfield Sibrel asked Buzz Aldrin, the Astronaut on Apollo 11, to swear on Bible that he walked on the moon. Enraged Aldrin hit him on the face. Time and tide being against the American government, naysayers had a field day and remained in news. Vietnam War and Watergate scandal had seriously eroded people’s faith in State Administration which appeared on the back foot in defending the veracity of Apollo expeditions.
Apollo 11, as a matter of fact, is easy to understand. Let’s begin with the missing tapes. Though only 450 tapes could be found and 4550 remained untraced, bona fides of NASA and the American government can’t be doubted. For, if there were a mala fide attempt at destroying them, even 450 wouldn’t have been found, and the state wouldn’t have supported team searching for the missing tapes.
Is moon landing just a hoax?
Why no stars were visible in lunar photos? Well, just as they are not visible on earth in daytime. How did Astronauts survive radiations of Van Allen Belts? Simple, they took care to avoid hotspots of this belt and navigated through a safe zone. That apart, Apollo 11 was fairly insulated against radiations.
Videotapes of men walking on the moon are fuzzy and indistinct; why? The answer is the underdeveloped technology of that time. Cameras captured images on a slow scan format so that space on Broadcast Spectrum could be saved for important communications. Sceptics laughed saying shadows in photographs were bizarre. That, they said, indicated shifting of arc lights for on-stage photo-shoot. Scientists explained that objects photographed on snow-covered hills, rough and uneven surfaces are bound to have shadows of varying dimensions.
How did flag flutter when no wind blew on moon surface? Well, flag fabric was supported with metallic wire to keep it spread, in flying shape. Astronauts jumped in the air supported by thin wires, said, sceptics. The scientists argued that this was impossible calling attention to dust that rose with movement. Were it earth, rising dust would mingle in atmospheric air, creating a dusty cloud. But that being moon, the dust didn’t rise, but fell back on the moon surface.
The cameraman was nowhere seen in footages, how was the videography done then? Actually, the Astronauts had cameras tucked in their suite. The moon lander vehicle too was equipped with the camera. With the passage of time, problems faced by America were sorted out, the credibility of state restored and Apollo rumours petered out in face of consistent and logical rebuttal from state agencies.
Presently Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is circling around the moon, collecting images and scientific data, and collating it with findings of Apollo Mission. This project of NASA has put to rest many misgivings about man’s landing on the moon. Though doubts are still raised off and on, general opinion favours the stand of the scientific community. Man, doubtless, landed on the moon, claims to the contrary notwithstanding.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Lost Cosmonauts of USSR: Did the Soviet Union Cover up its Secret Cosmonaut Casualties?“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Did Man Really Land on Moon? The Dilemma of Apollo 11’s Missing Tapes appeared first on .
]]>The post The Mysterious Wow! Signal: Aliens? A Comet? Or Just a Glitch? appeared first on .
]]>
Scanned copy of the original document that detected the Wow! signal. (Big Ear Radio Observatory and North American AstroPhysical Observatory (NAAPO))
Volunteer astronomer Jerry R. Ehman was going through the recorded data of the Ohio State University‘s radio telescope, Big Ear and discovered a 72-second irregularity in the charts. Big Ear was being used to detect possible signals from intelligent life in outer space, and on August 15, 1977, it received a very strong signal from outer space, that lasted for a good 72 seconds.
Ehman was startled at this discovery and wrote “Wow!” in red on the printout, after encircling the reading. Pretty much the first word that any of us would say after knowing that there is probable proof of intelligent life beyond Earth. Needless to say, the signal since then has been called the Wow! Signal.
Evidence
Big Ear observatory relied on the Earth’s rotation to scan the skies. Estimations were made keeping in mind the speed of rotation of the Earth and the spatial width of the telescope, Big Ear was able to observe a given point for 72 seconds only.
Any constant extraterrestrial signal in such a case could be recorded for not more than 72 seconds, with the signal increasing gradually for 36 seconds as the telescope approached the point. The intensity would be at its peak, marking the centre of the observation window and then, start dropping as the telescope moved away from the point.
That is exactly what was depicted in the recording of the Wow! Signal. The signal was a narrowband continuous radio signal with no break in modulation and had supporting data to prove that it indeed came from interstellar space. The source of the signal was narrowed down to a space in the constellation Sagittarius, south of the 3-star cluster called Chi Sagittarii.
Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI)
SETI was established in the early 1900s for collective scientific study and search for extraterrestrial intelligent life in outer space. It was conducted by examining the electromagnetic radiations from other planets and stars for any signs of communication.
With the arrival of radio, it was believed that the radio could be used to contact Martians after Guglielmo Marconi declared that his radio had been able to detect signals from Mars which could be a possible message.
August 21 to 23 in 1924, Mars was closest to Earth and visible almost all night. During those 3 days, the United States embarked on a programme to detect and decode any potential Martian communication.
In March 1995, American physicist, John Daniel Kraus explained an idea of how the universe could be searched for any emitted radio signals. This was published in the issue of a popular American science magazine, Scientific American.
According to Kraus, this could be achieved by using a flat-plane radio telescope with a parabolic reflector. His concept was approved within 2 years and went underway with construction by the Ohio State University on a 20-acre plot in Delaware, Ohio. This Ohio State University radio observatory telescope named ‘Big Ear‘ started operating by 1963 and on August 15, 1977, was instrumental in the major breakthrough by Ehman.
Waiting for the recurrence of the signal
Ehman and several other astronomers tried to search for another emission from the same location using Big Ear but were unsuccessful in doing so.
The curiosity of the scientists in the Soviet was piqued during 1960s leading to innumerable searches for picking up radio signals from space. In 1962, a ground-breaking book on SETI, ‘Universe, Life, Intelligence’, by Iosif Shklovsky, a Soviet astronomer formed the basis for an expanded explanation in American astronomer Carl Sagan’s book, ‘Intelligent Life in the Universe‘ in 1966.
American astronomer Robert H. Gray tried to look for the Wow! Signal with the META array of Oak Ridge Observatory in 1987 and 1989, but was unable to find it.
In July 1995, American scientist and SETI League Executive Director H. Paul Shuch scanned the coordinates which were the origin of the Wow! Signal, with a 12-metre radio telescope in Green Bank, West Virginia, but to no avail. Robert H. Gray attempted yet again to search for the signal in 1995 and 1996, using the radically sensitive Very Large Array. The Wow! Signal or anything like it could not be found again.

Very Large Array observatory in New Mexico. (John Fowler / Flickr)
Wow! Signal: An alien communication or miscommunication by the Big Ear
Astronomer Professor Antonio Paris of St. Petersburg College in Florida, was taken in by the Wow! Signal phenomena and wanted to come to a conclusion. The more he thought about the source of the signal, the more it came to him that probably the signal was emitted from a comet or an asteroid. He started going through the archives to find all possible comets that had not been discovered in 1977 but may have been in the surrounding area of the constellation Sagittarius.
He published his findings in January 2016 in the Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences. According to him, Comet 266P/Christensen that was discovered in 2006 and Comet P/2008 Y Gibbs discovered in 2008, were somewhere within the constellation Sagittarius in August 1977. Paris stated that comets, sometimes, give out radio waves from the gases surrounding them.
Paris used a radio telescope to check the radio signals emitted from comets and found these to be at 1,420 MHz frequency, the frequency of the Wow! Signal.
On 25 January 2017, radio telescopes were positioned towards the area of the sky where the Wow! Signal had come from, as Comet 266P/Christensen was to pass through the area again. The comet however, went above the Wow! Signal location by 2 degrees.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Bloop: Large Mysterious Animal of the Deep Sea? or Ice quakes?“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post The Mysterious Wow! Signal: Aliens? A Comet? Or Just a Glitch? appeared first on .
]]>The post Truth Behind The Black Knight Satellite Conspiracy Theory appeared first on .
]]>
1998 photo of an unidentified object by NASA taken during Space Shuttle mission STS-88. (NASA / STS088-724-66)
Developed in the year 1899, the Black Knight Conspiracy theory is something that has taken everyone aback with its mystery game. If the alien technologies and source materials are to be believed, this theory stands perfectly true.
Discovered by Tesla, the Black Knight satellite is an unidentified object captured on camera by NASA astronauts. The theory states that the satellite is around 13000 years old and is orbiting the earth surface in the adjacent polar orbit. The first instance of its origin can be dated back to 1899 when Nikola Tesla performed some radio experiments.
However, in 1954, once again a UFO researcher named Donald Keyhoe reported that two satellites have been traced to be revolving around the earth’s surface (the first man-made satellite was launched only in 1957). In 1998, a space debris was photographed by NASA which appeared to be the same unidentified satellite. With so many speculations being rife about this conspiracy theory, you certainly might be curious to reach the truth. Here are all the facts we know about this theory.
Discovery of black knight debris
In the year 1901, Nikola Tesla talked about his experiments with electric current. He stated that while carrying out those experiments, he encountered some interferences in electric signals. He further concluded that these disturbances could be from an extraterrestrial source for establishing a communication.
After this incident, again a radio operator from Norway named Jorgen Hals detected long delayed echoes. However, the radio operator was unsure about the cause and reason of these echoes. If some theories are to be believed, these echoes were the same as discovered by Tesla.
Clyde Tombaugh’s ambiguous claim
During the Black Satellite appearance, the discoverer of Pluto, Clyde Tombaugh was at the University of New Mexico along with Lincoln Lapaz. Both of them were doing research on few unexplained phenomena and credibility of alien satellites. Though the discoverer denied any reports of seeing the Black Knight Satellite, his statement was reportedly quite cryptic.
Was it a Bracewell probe?
Both Tesla and Hals talked about signals which were supposedly coming from an intelligent source in space. In the year 1960, another theory was bought into the picture by Ronald Bracewell. Bracewell said that in order to establish a communication with earth, other life would likely feed a satellite with all the necessary information and then launch it into space.
Such probes should be capable of covering larger distances and hence can reach the planet it has been trying to communicate. If the facts are linked to each other, these transmissions could be the same as that discovered by Tesla and Hals.
The heated speculations
In February 1960, newspapers and magazines got flooded with yet another report of an anonymous satellite which was detected by the US military troop with unknown origin.
The popular TIME magazine came up with a news that the object was merely a retrorocket from a previously launched satellite. The year 1963 started with new claims about the satellite, astronaut Gordon Cooper saw a UFO cross the sky while he was orbiting Earth. Later, such reports continued to entangle the mystery of Black Knight satellite.
In the year 1974, Duncan Lunan, a Scottish science fiction writer claimed that LDE (long-delayed echoes) heard by Hals was from a star system Epsilon Boots. However, the only issue with this claim was that one of the stars from the Bootes constellation was said to be in the wrong place. He further claimed that the probe was nearly 13,000 years old.
STS-88 encounter-recent evidence
Though most of the evidence of black Knight Satellite has been dated back to the early 90’s. There has been a recent evidence from 1998 where the crew members of space shuttle named Endeavour captured an unusual object moving along the lower orbit of the earth.
These snapshots are considered as the most valid proof of the satellite presence. However, on the closer observation, the structure also bears an uncanny resemblance with space debris.
When the mission was conducted by Colonel Ross and Dr James Newman, they attempted to install some thermal blankets for storing the energy. However, as the blankets were linked to the spacesuit, one among them was gone. In actual, these objects are most supposedly a thermal blanket that got lost.

Close up photo of the space debris. (NASA)
Conclusion
Even after numerous claims about the Black Knight Satellite, there has been a major lack of evidence that can connect the LDE’s discovered by Tesla to the other discoveries made in 50’s and 60’s. However, it has become quite common for the conspiracy theorists to relate any unidentified object to the popular Black Knight satellite.
While some reports claim that the STS-88 sightings and UFO bear a striking resemblance with each other. Some other reports negate this claim and call it a mix of different reports about the Black Knight.
These myths about Black Knight Satellite is so confusing that it is now regarded merely a collection of random tales.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Did Man Really Land on Moon? The Dilemma of Apollo 11’s Missing Tapes“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Truth Behind The Black Knight Satellite Conspiracy Theory appeared first on .
]]>The post Gliese 581g: A Habitable Exoplanet or Just Another Celestial Object Orbiting a Star? appeared first on .
]]>
Artistic rendering of Gliese 581c discovered before Gliese 581g which was also regarded as a potentially habitable planet in 2007. (Kobol / Celestia)
Recently, a probe has been sent in space that will, for the first time, get a closer look at the Sun’s surface and bring back information related to the massive ball of fire. Anything space-related immediately becomes a hot topic of discussion back on our planet, yet it happens to be one of the most intriguing subjects.
After space explorers discovered the presence of water beneath the surface of Mars a couple of weeks ago, this was not the first time humans found a potential source of life on another planet outside our solar system. However, newer claims could not be completely confirmed and the more-than-a-decade-old discussion of a habitable extrasolar planet might only be a case of wishful thinking.
Ten years ago in 2008, a group of researchers and astrophysicists at the University of California and Carnegie Institution of Washington together came up with an astonishing discovery outside our planetary system. Weighing about three times more than the Earth and falling into a habitable zone, a planet was located approximately 20 light-years away that could possibly sustain life just like the Earth can.
Orbiting a dim red dwarf star, the planet was named “Gliese 581g” or Zarmina (named after the lead discoverer’s wife) by the researchers. The solar system named Gliese 581 is made up of a lesser hot (as compared to the Sun) star, around which four or more planets, including Gliese 581g circle in a gravitationally-locked position.
The lead astronomer Dr. Steven Scott Vogt and co-researcher R. Paul Butler theorized the presence of habitable conditions on Zarmina for more than a decade, which came as good news to many. By the year 2012, more researches confirmed its existing status, but observations and reanalysis put its existence in jeopardy once again in 2014. Now, as recently as 2015, when Dr. Steven Vogt presented some more substantial findings, a consensus was reached that the new planet could still exist in another solar system.
About Gliese 581g
Lying right in the middle of its planetary system, Zarmina has a rocky surface, beneath which there could be the presence of streams of water. It has a dense atmosphere, which could make it possible for life to sustain in hospitable conditions. As per Dr. Vogt’s research findings, the idea of human habitation on Zarmina is too far-fetched for now, but if the planet is potentially habitable, liquid water could possibly be the source of supporting life on its surface.

Comparison between our solar system and Gliese 581 planetary system. Where g indicates Gliese 581g. (Zina Deretsky / National Science Foundation Press Release 10-172)
Gliese 581g has temperatures ranging between minus 24 degrees Celsius to 10 degrees Celsius, which is not too hot and not too cold as far as harbouring life matters. The exoplanet orbits its star in a nearly-circular motion in around 37 days and is in a gravitationally-locked position with its parent star. It can be best described as people seeing only one side of the Moon from Earth from any part of the world, while the far side always remains in the dark.
Its surface gravity is 1.1g as compared to the Earth’s, which is 1.7g. Since its parent star is a lot cooler than our Sun, the planets in Gliese 581 are clustered closely together to obtain energy and warmth, so that water can be maintained in its liquid state on its surface.
Doubts over its existence
While researchers from Washington and California were quite positive about their results, which they had gathered from the HIRES or High-Resolution Echelle Spectrometer – an astronomical observatory in Hawaii; research team led by Dr. Michael Mayor of Geneva Observatory maintained that their extensive study did not detect any such exoplanet and thus cast a long shadow of doubt on Gliese 581g’s existence.
Another astronomer Francesco Pepe, who worked on The HARPS or High Accuracy Radial velocity Planet Searcher situated in Chile, came up with 6 years of research, which contradicted with Dr. Vogt’s findings, thus questioning his claims of a potentially hospitable extrasolar planet in the already long list. Also, Dr. Mayor suggested that they could only collect data material on planets Gliese 581a, b, c, d and e on their systems, and the proof of Gliese 581g’s existence could never be gathered, thus brushing aside his discovery.
The number of Dr. Vogt’s non-supporters only kept increasing, with many of them presenting their own facts, opposing the lead scientist. A former student of Dr. Vogt, Artie P. Hatzes, currently associated with Thuringia State Observatory in Germany, challenged his mentor’s research, yet had his own doubts. He stated that based on his own findings, there may or may not be a Gliese 581g in the first place, which makes the theory of its habitability almost uncertain.
Another researcher, Rene Andrea from the Max Planck Institute of Astronomy in Germany, also raised questions over Dr. Vogt’s study, stating that when his team ran simulations, they found that Dr. Vogt’s team had incorrectly drawn conclusions regarding Gliese 581g’s circular orbit.
Philip Gregory from the University of British Columbia submitted his papers that hinted at the new solar system having only four planets and ruled out Gliese 581g’s existence altogether. His team also wound up their research mentioning that Gliese 581g may not be a real planet after all.
A postdoctoral research student at Penn State University, Paul Robertson also disregarded Dr. Vogt’s study stating that the presence of Gliese 581g was based on the orbital activity of 581d. He also stated that sunspots sometimes act like planetary signals and that could have altered Dr. Vogt’s findings.
While Dr. Steven Vogt kept defending his celestial investigation, with media and other researchers holding on to the hopes highly, the fate of Gliese 581g, gaining status of a habitable world, is yet to be sealed.
Researchers are keeping a close watch on the skies as more information keeps coming in regarding the newly-found planet, the existence of which has become a matter of dispute. There is still so much to explore in the deep outer space and it is only a matter of time before we get to know whether Gliese 581g makes the cut in the hospitable exoplanet list or not.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “ʻOumuamua: A Mysterious Interstellar Rock Discovered in Our Solar System“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Gliese 581g: A Habitable Exoplanet or Just Another Celestial Object Orbiting a Star? appeared first on .
]]>The post What Would Happen if Solar Storm of 1859 Occurred Today? appeared first on .
]]>
Artist rendering of Solar Storm striking earth’s magnetic field. (NASA)
Sun, the furiously spinning fireball in cosmos is central to the survival of planet earth. It is made up of plasma, the fourth state of matter, formed when atoms get broken down to protons and electrons. These charged particles make plasma an extremely good conductor of electricity and sun, on the whole, a warehouse of electromagnetic radiations. Corona, the least dense and outermost layer of Sun has a temperature of 500,000°C. Imagine this hot ring spinning off (coronal mass ejection or solar flare or solar storm) and hitting a part of planet earth. This happened on September 1, 1859; on May 23, 1967 and can happen again any time in future.
Solar Storm of 1859
Foreshadow of 1859 electromagnetic whiplash (sun strike) was caught by English Astronomer Richard Carrington on his telescopes on September 1, morning time. He saw 2 bright white blobs emerge from sunspots and disappear in 5 minutes. By night time the impending calamity manifested physically with a strange play of bright lights, of various colours, sequencing one after the other in the sky. This blaze of light was beguiling, weird and frightening.
That night, telegraphic communications went bust. Sparks flew from operating machines, burning paper loads. Sky illuminated so brightly, it looked like sunrise. Many started their morning chores thinking it was dawn. Others thought the world was coming to an end. Birds started chirping as they do when the day begins. It was on-earth manifestation of billions of tons of electromagnetic particles hitting earth, foreshadow of which Richard Carrington had seen through his telescope in his private observatory near London. It was a solar storm, backed by the power of 10 billion atomic bombs; electrified gas and subatomic particles bombarding earth. Aptly named ‘Carrington Event’, this is the largest such event recorded in the history of astronomy. Information systems of those days may be archaic compared to today’s internet era, nonetheless, damage caused to them was sanguine, significant and shocking.
Trailing the above ‘Carrington Event (CE)’ were the 2 solar storms hitting America on the night of 28th August. Recalling event, E.W.Culgan, telegraph manager in Pittsburgh said that current in wires was so high that it could melt platinum joints in the communication system. Ground circuits spewed fire relentlessly. In Washington, a telegraph operator singed his forehead from sparks flying off the cable.

The solar eruption which leads to coronal mass ejection. (NASA Goddard Space Flight Center)
CE continued well into 2nd September 1857. At 8 AM employees of American Telegraph Company found it hard to send or receive messages. On the flip side, some messages (to Portland, Maine) could be transmitted intermittently even as circuit batteries were turned off, all thanks to currents produced when charged particles from sun interacted with particulate matter in earth. It wasn’t before 10 AM that disturbances subsided and the batteries were again switched on.
People in France to Australia saw flashes of crimson red, bright enough to turn night into daytime. Many thought that blazing fire somewhere near had caused it. Northern lights (Aurora Borealis-green electric flashes that generally seen in the northern hemisphere) showed an unusual shift to the equator and became visible in Cuba and Jamaica. In Abbeville, South Carolina, construction workers got up from the bed and began working thinking it was sunrise, but went back to sleep realizing light in night time was freak of nature. In Bealeton, Virginia, birds chirped and fluttered at 1 AM. People across America came out on street to watch the brightly lit sky. In Boston, people were seen reading newspaper in the burst of unusual light.
What if such an event was to occur today?
Investigations have revealed that Carrington Event was twice the magnitude of any other solar storm happening in the past 500 years. If such an event happens now in today’s internet age, consequences are bound to be several times more devastating. In fact, it would be a complete disruption of communication systems and services leading to a long-lasting disorder and chaos worldwide. GPS systems, Satellite Communications and power grids would be smothered by waves of plasma waves surging from sun surface.
In terms of money total loss world over maybe to the tune of 2 trillion. Quebec blackout of March 13 1989, makes a good case study for such possibility in future. Even though only one third as strong as CE of 1859, it smashed a power grid of 6 million consumers in just 2 minutes. Storm as powerful as CE can destroy an entire lot of transformers in power company godowns. This would mean a death knell for most civic and telecommunication facilities till new transformers manufactured and pushed into service.
Confusion during Solar Storm
As for solar storm of 1967, it almost became a flashpoint of nuclear war between America and Russia. On May 23, 1967, US military’s Ballistic Missile Early Warning System (BMEWS), meant to detect incoming Soviet missiles, was disrupted by a solar storm. Those were the days of cold war between these 2 super powers and US aircrafts routinely carried out sorties with aircrafts loaded with nuclear weapons.
Glitch in the system, caused by Coronal Mass Ejection was tentatively viewed as wanton sabotage by Russia Forces. By implication, it was an act of war and prompted American air force to deploy more of nuclear weapon aircrafts in ‘ready to strike’ mode.
Thankfully, North American Aerospace Defence Command (NORAD) detected the problem timely and informed all concerned that the BMEWS disruption caused was caused by solar storm, and not the Russian forces. But for this information conveyed to Air Force Commanders in the nick of time, US nuclear aircrafts would have taken off for hit and it would have been very difficult to communicate with them mid-air because of solar flare.
A counter from Russia would have inevitably followed throwing the world into nuclear war with wide-ranging tragic consequences. This geomagnetic storm began 40 hours after solar bursts and played havoc with U.S. radio communications for one entire week. Rated top-notch geomagnetic disturbance in record books, it is still no match to CE 1859 that failed telegraph communication in entire North America and Europe and stretched the reach of Northern Lights right up to the Caribbean.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Pale Blue Dot: The Iconic Photograph Showing How Microscopic But Brilliant Earth Is“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post What Would Happen if Solar Storm of 1859 Occurred Today? appeared first on .
]]>The post Zinnia, The Prodigal Flower of Bonhomie Between Life in Space and Life on Earth appeared first on .
]]>
Photo of the first Zinnia flower in space. (NASA / Wikimedia Commons)
Space outside of Earth’s gravitational field has been explored so intensively and extensively that now the next logical step is human habitation in space. That obviously can’t happen without plants; which are required fresh food, visual euphoria and life-sustaining oxygen pool in the environment. The International Space station (ISS) was launched in orbit in 1998 by National Aeronautic and Space Administration (NASA), USA for space exploration, scientific discovery and aeronautics research.
Soviet Salyut 7 space station, 1982, conducted the first successful experiment in growing plants in space up to flowering and was successful in harvesting next-gen seeds from seeds grown in space. By 2003 the Russian Cosmonauts were not only experimenting on space crops but also consuming them as food. Allan H Brown, had already proved in 1983 that growth in plants/seeds was innately controlled, not environmentally influenced/dictated.
Establishment of Vegetable Production System (Veggie) by ISS in 2012 was a milestone development. Veggie unit is a container with in-built mechanisms, plant pillows, to guide plant growth. Plant Pillows include bags of manure, dirt, nutrients and a water absorbing wick. Seeds are glued to wick in a way their roots grow towards the bottom of the bag and the stem upwards. LED lights above the arrangement provide energy for plant growth and the growing leaves are cushioned by the flexible and expandable walls of Veggie. This system has focussed on salad vegetables like lettuce, Swiss chard, radishes, Chinese cabbage and peas which could be easily plucked and eaten as-such by the Cosmonauts.

Plants growing in Veggie unit on ISS. (NASA / Wikimedia Commons)
On August 10th 2015, American Astronauts ate their self-grown Red Romaine Lettuce. Blooming of sunflower in 2012, and Zinnia in 2016 were landmark achievements. Zinnia’s success was significant as it paved way for long-duration and fruit-bearing crops like tomatoes, peppers, strawberries, beans and peanuts. Growth duration of 60-80 days and upscale sensitivity to the environment made space cultivation of Zinnia extremely challenging. Just 2 weeks into their growth, zinnias showed curling of leaves and droplets of water on leaf margins; typical stress symptoms. High-speed fans were used to control humidity that caused mold outbreak. Dedicated efforts of the crew, Scott Kally in particular, bailed plants out of the problem creating a milestone in space agricultural technology.
Observations and disproving Darvin’s hypothesis
Formation and orientation of plants in zero gravity situation was an interesting observation. Skewing root growth hypothesis of Charles Darwin held that gravity and environment decided plant growth on earth. With seeds showing skewing growth patterns in space as well, Darwin’s hypothesis was disproved. Studies finally concluded that plants changed their gene expression in the no-gravity situation. It is like plants can sense departure in their environment and adjust accordingly.
An extra-terrestrial environment can stress plants in many ways. Apart from temperature, light and available nutrients, plants are impacted by changes in gravity, radiations and gaseous exchange. These factors trigger reprogramming of gene expression to adjust to the hostile environment. An understanding of this genetic programming, courtesy Biological research in Canister (BRIC) is a giant step towards space agriculture as well as the life on earth.
How are earthlings benefiting from the research?
A related program of ISS, Lada Validating Vegetable Production Unit – Plants, Protocols, Procedures and requirements uses a chamber, like a greenhouse, with auto control for water and light. It is an on-earth research lab for assessing food value of space crops, identifying and controlling microorganisms that harm these crops, sanitization of crop produce post-harvest and optimization of plant production in space conditions. Interestingly research applies as well to life on earth as on space.
Air purification technology designed primarily for space stations is also being used to keep air in household clean and healthy. A leaf sensor developed for long-duration space missions is being used by farmers to conserve water, as it indicates the right time when plants are `thirsty’. A common problem both on earth and space is ethylene, a gas emanating from plants which speeds up the ripening of fruits and vegetables. Hastened ripening leads to faster decay. The solution lays in neutralizing ethylene and came by way of ethylene scrubbing technology.
But technology did much more than just destroy ethylene. It simultaneously destroyed many airborne bacteria, fungi, molds, mycotoxins, viruses and undesirable odours. Now, these scrubbers are being used widely in food preservation and processing plants, wineries, restaurants, refrigerators, and deodorants. Doubtless, research at NASA is not just for space exploration. Its importance for life and business on earth is as sanguine. Robotic surgery is a gift of space research. So also telemedicine and medical intervention through remote control.
Can breathe analysis be a way to detect dormant/insidious disease processes?
Yes, thanks to the technique of calibrating Nitric Oxide in air exhaled by Astronauts. Men in space and elderly on earth, both suffer from weakening of bones. Use of bisphosphonate, low sodium diet and exercise has proved useful for both. The study of plasma (charged gases which can permeate matter quickly and even spread evenly) has proved as effective in medical treatment as in plant growth. Studies on microgravity have given important leads for treatment of immunosuppression.
Development of microencapsulation for targeted treatment of cancerous growth and dry immersion technology for early diagnosis of neurological disorders, oedema, sports medicine and rehabilitation of premature babies are all thanks to space research. Study of cardiovascular system on space flight has guided us on how to examine health parameters of motor vehicle drivers and civil aviation pilots. Studies on motor disturbances in zero gravity is being used to treat patients with cerebral palsy, stroke, spinal cord injury and age-related motor disturbances.
With plants as company on the space mission, it is safe to assume that crew would feel more comfortable in staying for months, even years and wouldn’t tax their physical and mental health as is likely without such company. Space research in the meanwhile is extending a yeoman service to humankind, even before the dream of colonising space for human dwelling becomes a reality.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Space Food: What Do Astronauts Eat Outside the Earth’s Atmosphere?“.
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Zinnia, The Prodigal Flower of Bonhomie Between Life in Space and Life on Earth appeared first on .
]]>The post Space Burial: Making Skies Our Cemetery appeared first on .
]]>
Space Burial: Photo of Earth from Space. (NASA)
As kids, most of us have thought of becoming an astronaut, floating in zero gravity, operating complex space shuttles and looking at our beautiful big blue planet from a distant. But most of us gave up on that thought as we grew up. While we can still take a trip to outer space to fulfill our dream, it will cost us a few million dollars. But, don’t lose hope yet, there are several companies that are willing to take you to space for as low as $1295, the only criteria is that you have to be dead.
Space burial or space funeral involves carrying of cremated ashes of a person to outer space. However, the ashes aren’t scattered in space, rather they are encapsulated into a specially designed capsule container which is integrated into a spacecraft taking them to space.
Space burial package and services
Amongst the private companies that offer the space burial service, two giants, Celestis and Elysium Space form a duopoly. They offer several packages to choose from. These packages start from $1295 for basic outer-space experiences providing five to six minutes of weightlessness and go as high as $12000 for an everlasting deep space experience. These packages also include a live broadcast of the rocket countdown and the service to effortlessly track the satellite while it orbits our planet.
Apart from the above experiences, people can choose two other experiences as well. These are the “Earth Orbit Service”- in which the remains of the deceased, orbit our planet for a limited duration before returning to earth as a shooting star and the “Luna Service”- in which the cremated remains are laid on the surface of our closest neighbour – the Moon.
People buried in space
Two Celestis mission satellites, “Celestis 03, The Ad Astra Flight” and “Celestis 04, The Millennial Flight” which were launched in 1998 and 1999 respectively are still in orbit and are expected to remain so for another 220 years. While there are several notable personalities including James Doohan (well-known for his role as Scotty in ‘Star Trek’) and Gene Roddenberry (creator of ‘Star Trek’) orbiting earth, there are only two people who have made it beyond the orbit.
The ashes of Dr. Eugene Shoemaker, a prominent astronomer, were carried by Celestis’s Luna Service 1 and rests on the surface of our natural satellite. The second person to make it beyond the orbit is Clyde Tombaugh, an American astronomer who discovered Pluto in 1930. His ashes are aboard the NASA’s “New Horizons” which passed Pluto in July 2015.
The history of space burial can be traced back to the early 1930s when the idea was first circulated in a novel by Neil Ronald Jones. In 1965 movie, ‘The Loved One’, this idea was commercially projected for the first time. While several developments were made in the 1980s, the first space funeral was conducted in 1992 when NASA’s space shuttle Columbia carried few portions of Gene Roddenberry’s ashes into space.
Celestis became the first company to conduct private space funeral in 1997. Named ‘Celestis’ Earthview: The Founders Flight’, the mission carried remains of twenty-four people including Gene Roddenberry, Timothy Leary, Gerard O’Neill, Krafft Ehricke in a ‘Pegasus’ rocket which orbited the earth for 5 years before returning to Earth.
Enjoyed this article? Also, check out “Neptune Memorial Reef: An Eco-Friendly Underwater Graveyard Off the Florida Coast“.
Official Websites:
1. Celestis: Memorial Spaceflights – Space Funeral Ashes Burial
2. Elysium Space | Ashes into Space | Memorial Spaceflights
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Space Burial: Making Skies Our Cemetery appeared first on .
]]>The post Laika the Canine Cosmonaut – From the Streets to the Stars appeared first on .
]]>
Laika training for her expedition. (NASA)
We all know the names Buzz Aldrin and Yuri Gagarin for being – conspiracies aside – some of the first people into outer space. Gagarin from Russia is considered the first man to orbit Earth in 1961 and in 1969 the Americans: Aldrin and co-pilot Neil Armstrong set foot on the moon. They paved the way for what is now a golden age for space travel with ideas hatching for passenger flights and plans to colonize other planets. But who paved the way for them?
Less is known about their counterparts, animal astronauts who have also voyaged – albeit forced – into the unknown, many in the name of the Space Race between the aforementioned countries. The most famous of these was a little Russian dog called Laika. In a time when conditions in space were unknown, Laika was chosen as a Guinea Pig before any human had made the jump. She was picked from the streets of Moscow to join the Russian space mission Sputnik II in 1961.
Why Laika?
According to the crew, Laika was around three years old, a mongrel female and unlike her name suggests [Barker] remained very quiet. Found in the Russian capital, her exact breed is unknown but almost certainly a cross between a terrier and some type of husky. Stray dogs were commonly used in previous preparatory missions because they can handle severely cold conditions and are ultimately less demanding.
The program picked a small female in terms of space-saving (for a spacecraft about the size of a washing machine, even leg-lifting was a factor). The good-natured mutt was quickly loved, birthing several Russian nicknames including Kudravka meaning Curly, Damka – Little Lady and Limonchik for Little Lemon. Muttnik would be her catchy handle in the English speaking world.
Read more: The story of the first primate in space that paved the way for manned spacecrafts.
The spacecraft Sputnik II would launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in modern-day Kazakhstan to test various cosmic conditions as well as the effects of space travel on an animal. The first Sputnik mission proved a success in orbiting the Earth and the second vowed to go further with a living creature in tow. Ultimately, Laika was a precursor to Yuri Gagarin, whose mission was already in the pipeline. Previous missions had also included dogs but they only reached suborbital conditions, this was to be a major step up. Veteran pups of those missions including a hound called Albina were to be backups. (Rumours say the crew got too attached)

Model of Sputnik 2 in which Laika travelled to space. (Laika ac / Flickr)
Preparation for launch
As launch day approached the darkness of the voyage soon began to sink in and there were protests around the world regarding the lack of humanity in proceedings. Such a mission today would cause an uproar, especially with the training which was brutal and by modern terms completely inhumane.
However, it was a different time back then, especially behind the Iron Curtain, with fewer objections aided by Cold War secrecy, Space Race obsession and a lack of Red Tape. Presumably, there would have been more protestation if people knew the truth. The truth that returning to Earth was never planned for Laika (a secret kept until 2002).
The crew have spoken more about this in recent times. They claim that the Soviet Union leader at the time, Nikita Khrushchev urged them to speed up the mission to coincide with the 40th anniversary of the Bolshevik revolution. It made several plans impossible to complete but Khrushchev was not a man to deny. In what was a cruel mission it is clear to see that the crew came to love the dog, whilst having to remain professional. They made a plan to euthanize her with a poisoned last meal if she suffered too much. They also made her a window. One scientist and trainer, Dr.Yazdovsky wrote that he took Laika home to play with his children on the night before launch.
“Laika was quiet and charming… I wanted to do something nice for her. She had so little time left to live.” he said.
Laika in space
The next morning was a Red Letter Day as the crew lamented and said their goodbyes. Sputnik II launched. Everything on board was monitored including Laika. At the start of the expedition, her heart understandably raced as the craft left Earth’s atmosphere but soon after, she started to calm. Her heart slowed and she continued to relax once reaching weightlessness. For the first time ever, a living being was orbiting Earth. She had made history. Within her harness, floating in Zero Gravity, Laika would have seen the blue and green of Planet Earth the way no-one had seen it before.
Perhaps she knew it was trees and water. Of course, the dog would be oblivious to the incredulity of events, and there is no doubt it was a traumatic experience but at least Laika felt some relief shown by her breathing. She even had some food before disaster finally struck. Her little heart started to race again and as temperatures rose, her panic took over. Eventually, there was no pulse detected and she was at peace.
The technicalities of her death are varied, it is simply claimed that overheating due to certain machine failures occurred approximately five hours into the flight. Laika’s death would have been a relief, also to many of the scientists once problems arose. The capsule became her coffin and after five months and over 2,000 orbits, they disintegrated upon reentry to Earth in 1958.
Later developments
Her death did not go unnoticed. Future space missions carrying animals were immediately made to be recovered after Laika’s death weighed heavy on the national conscience. As time went on more reforms took place and the callousness of the mission has forced many people to look back with regret none more so than the crew. Oleg Gazenko explains,
“Work with animals is a source of suffering to all of us. We treat them like babies who cannot speak. The more time passes, the more I’m sorry about it. We shouldn’t have done it … We did not learn enough from this mission to justify the death of the dog.”
Making such a difference for the greater good of the world would have been lost on Laika but she contributed more than most to the development of our world. Perhaps not in terms of aeronautics or space exploration but for animal rights and awareness, the little terrier became a martyr.

Laika on a Romanian stamp from 1959. (Wikimedia Commons)
She made the world remember that whatever we can achieve, we must do so humanely. She lives on in Star City, Russia, at the Russian Cosmonaut facility. There, a statue has been erected while all around the world Laika has been immortalized on items from posters to stamps.
Read more: Sex in space – is it possible? and why it is important
Recommended Read:
Soviet Space Dogs | Olesya Turkina
Recommended Watch:
Soviet Space Dog | BBC
Recommended Visit:
Science Museum | London
Fact Analysis:
STSTW Media strives to deliver accurate information through careful research. However, things can go wrong. If you find the above article inaccurate or biased, please let us know at [email protected].
RELATED
The post Laika the Canine Cosmonaut – From the Streets to the Stars appeared first on .
]]>